Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Diabetes. Feb 15, 2024; 15(2): 287-304
Published online Feb 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i2.287
Published online Feb 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i2.287
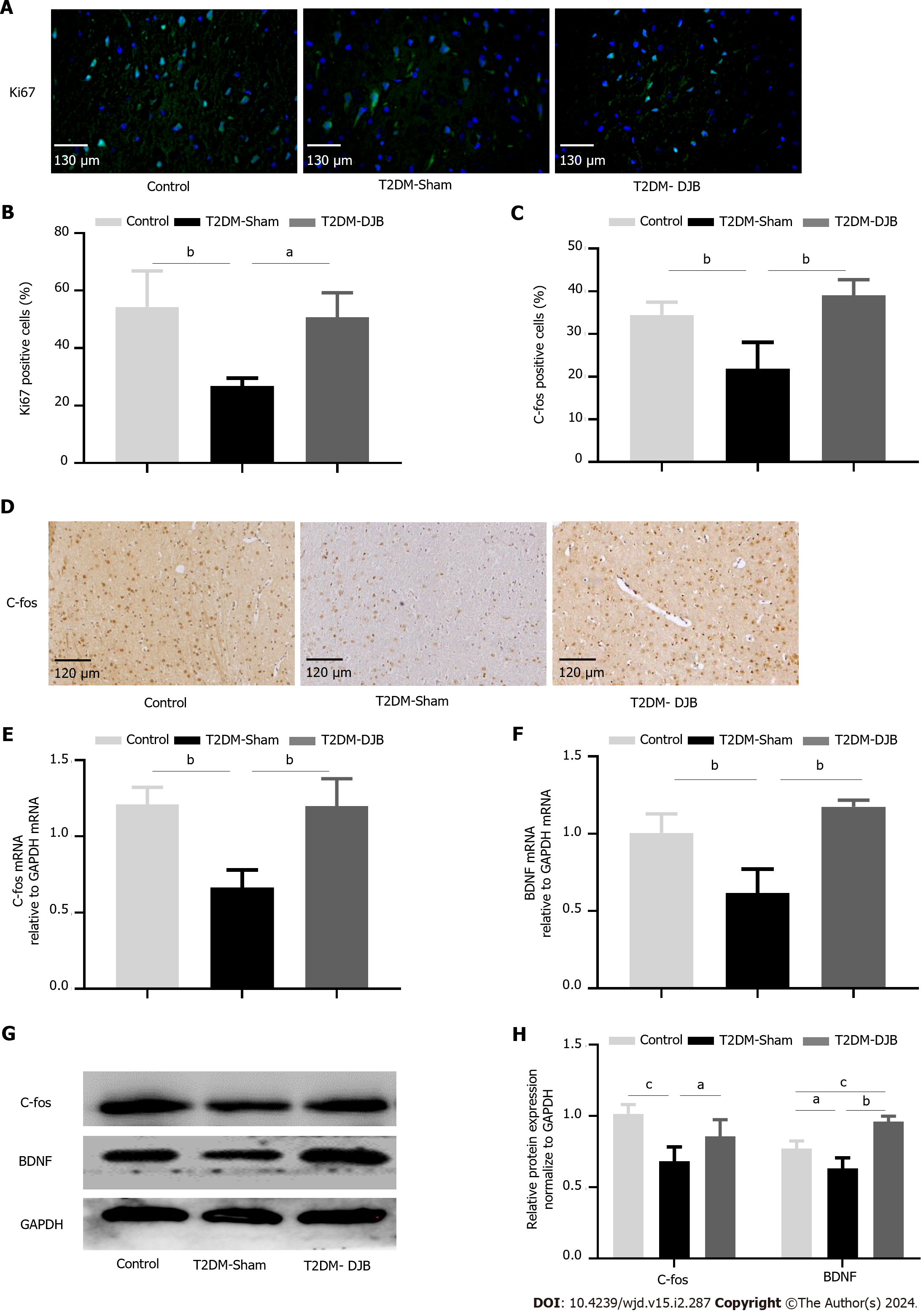
Figure 7 Duodenal jejunal bypass surgery promotes hypothalamic neurogenesis in type 2 diabetes mellitus rats.
A: Immunofluorescence analysis the expression of Ki67 (scale bar, 130 µm); B: The percentage of cells expressing Ki67; C: The percentage of cells expressing C-fos; D: Immunofluorescence analysis the expression of C-fos (scale bar, 120 µm); E: The quantitative real-time (qRT)-PCR results of C-fos expression; F: The qRT-PCR results of BDNF expression; G: Expression levels of C-fos and BDNF detected by Western blotting. The quantitative densitometric analysis of C-fos and BDNF. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. T2DM: Type 2 diabetes mellitus; DJB: Duodenal jejunal bypass.
- Citation: Wang HJ, Zhang LB, Sun SP, Yan QT, Gao ZQ, Fu FM, Qu MH. Duodenal-jejunal bypass improves hypothalamic oxidative stress and inflammation in diabetic rats via glucagon-like peptide 1-mediated Nrf2/HO-1 signaling. World J Diabetes 2024; 15(2): 287-304
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v15/i2/287.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v15.i2.287