Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Diabetes. Feb 15, 2024; 15(2): 275-286
Published online Feb 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i2.275
Published online Feb 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i2.275
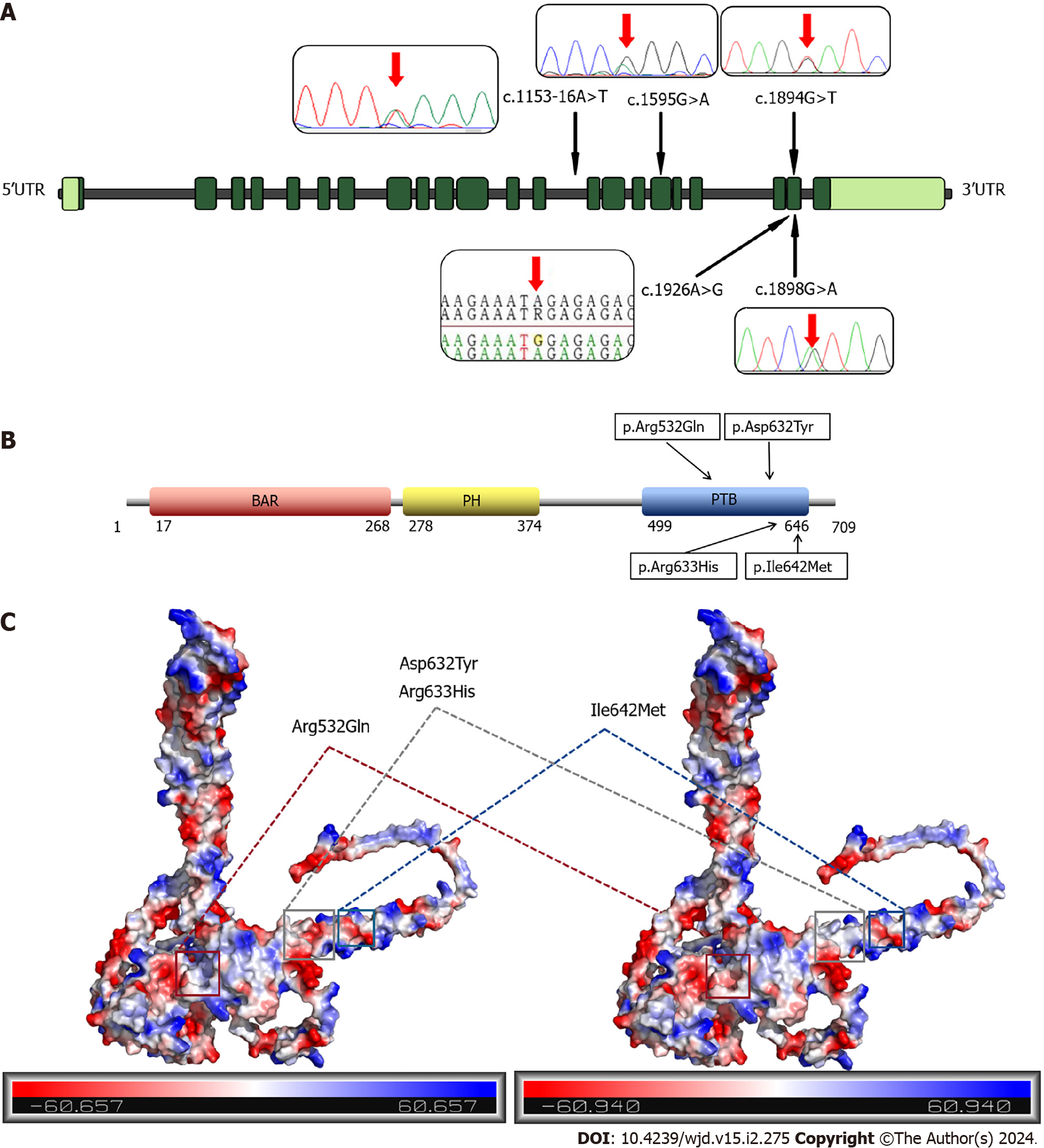
Figure 2 Distribution of mutation sites in adaptor protein, phosphotyrosine interacting with PH domain and leucine zipper 1 and adaptor protein, phosphotyrosine interacting with PH domain and leucine zipper 1 protein and potential changes in mutation sites.
A: Exon and mutation site distribution of adaptor protein, phosphotyrosine interacting with PH domain and leucine zipper 1 (APPL1) gene; B: Domain and mutation site distribution of APPL1 protein; C: Potential change of mutated APPL1 protein. BAR: Bin-Amphiphysin-Rvs; PH: Pleckstrin homology; PTB: Phosphotyrosine-binding; UTR: Untranslated region.
- Citation: Shi P, Tian Y, Xu F, Liu LN, Wu WH, Shi YZ, Dai AQ, Fang HY, Li KX, Xu C. Assessment of pathogenicity and functional characterization of APPL1 gene mutations in diabetic patients. World J Diabetes 2024; 15(2): 275-286
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v15/i2/275.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v15.i2.275