Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Diabetes. Oct 15, 2024; 15(10): 2093-2110
Published online Oct 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i10.2093
Published online Oct 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i10.2093
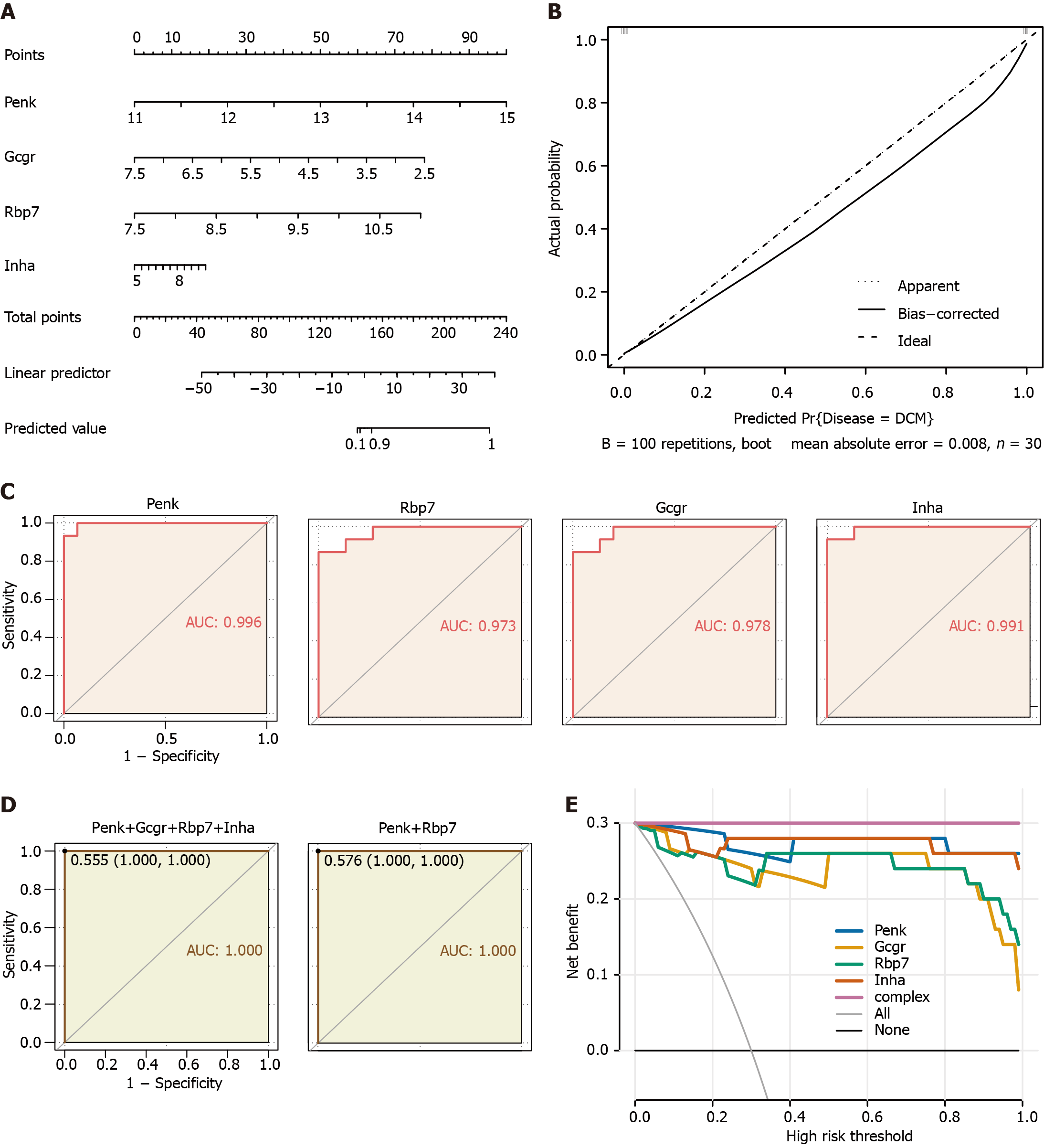
Figure 4 Clinical prediction models and diagnostic value for immune feature genes in the validation cohort.
A: Nomogram predicting disease risk by proenkephalin (Penk), glucagon receptor (Gcgr), retinol binding protein 7(Rbp7), and inhibin subunit alpha (Inha); B: Calibration curves visually assessing the risk nomogram model calibration, a key aspect of model validity; C: Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis of immune feature genes in diabetic cardiomyopathy (DCM) patients; D: ROC analysis of the diagnostic value of multivariable (four feature genes, unregulated Penk and Rbp7) in DCM patients; E: Decision curve analysis model construction was performed using a simple logistic regression model with Penk, Gcgr, Rbp7, and Inha as independent predictors and DCM as the outcome; a complex model (complex) was constructed by combining the four genes as predictors. Penk: Proenkephalin; Gcgr: Glucagon receptor; Rbp7: Retinol binding protein 7; Inha: Inhibin subunit alpha.
- Citation: Zheng ZQ, Cai DH, Song YF. Identification of immune feature genes and intercellular profiles in diabetic cardiomyopathy. World J Diabetes 2024; 15(10): 2093-2110
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v15/i10/2093.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v15.i10.2093