Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Diabetes. Oct 15, 2024; 15(10): 2093-2110
Published online Oct 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i10.2093
Published online Oct 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i10.2093
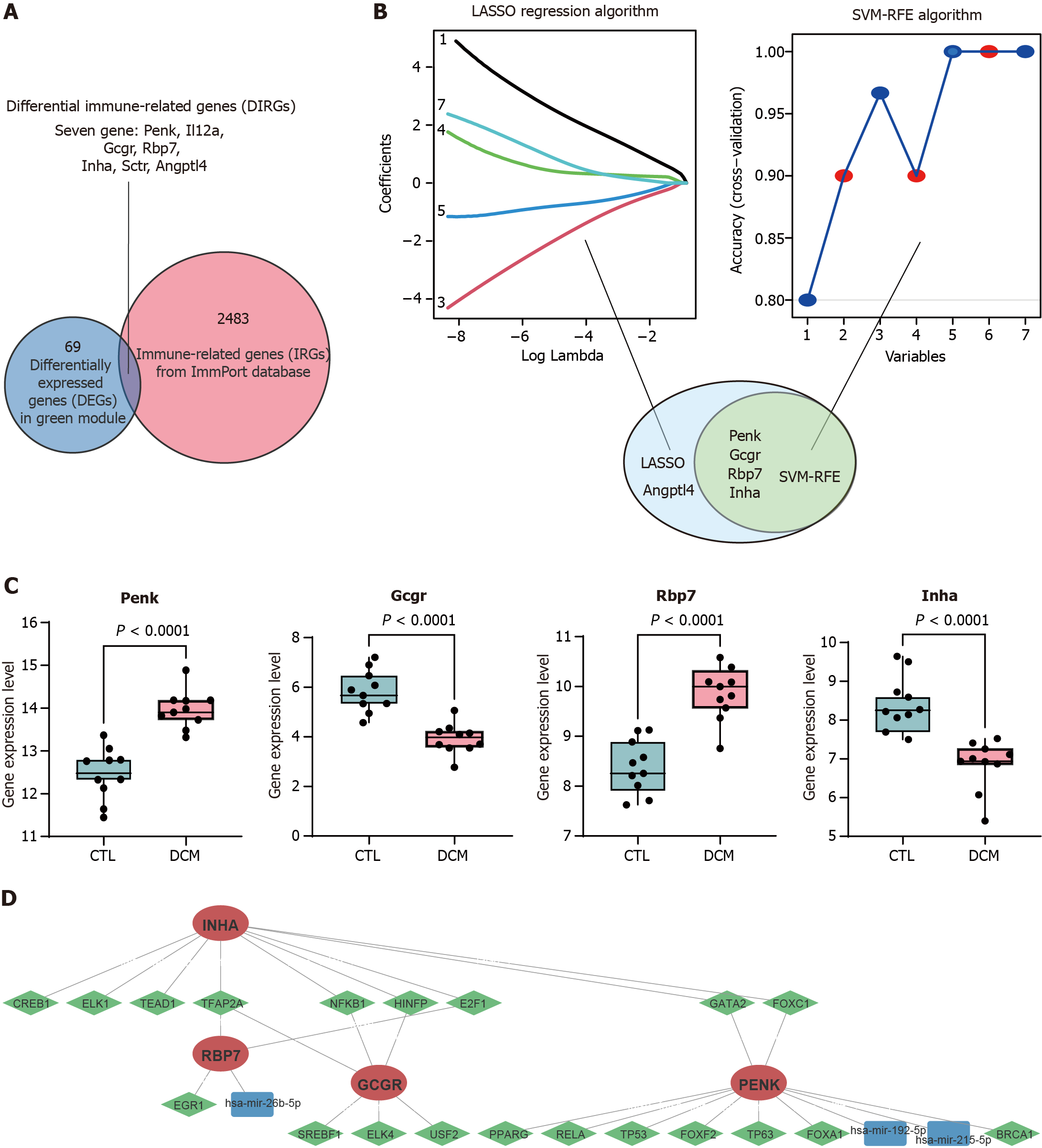
Figure 3 Identification of immune feature genes.
A: The differentially expressed genes in the green module were intersected with the list of immune-related genes from the ImmPort database to obtain 7 differential immune-related genes; B: Machine learning algorithm based on least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) and support vector machine recursive feature elimination (SVM-RFE) to select immune feature genes (IFGs) of diabetic cardiomyopathy (DCM). LASSO identified and selected 5 genes, whereas SVM-RFE identified and selected 4 genes; C: Box plot comparing the expression levels of the four common IFGs identified by LASSO and SVM-RFE between DCM patients and control patients; D: Gene expression regulatory networks. Red indicates target genes, green indicates transcription factors, and blue indicates miRNAs. LASSO: Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator; SVM-RFE: Support vector machine recursive feature elimination; DCM: Diabetic cardiomyopathy; CTL: Control; Penk: Proenkephalin; Gcgr: Glucagon receptor; Rbp7: Retinol binding protein 7; Inha: Inhibin subunit alpha.
- Citation: Zheng ZQ, Cai DH, Song YF. Identification of immune feature genes and intercellular profiles in diabetic cardiomyopathy. World J Diabetes 2024; 15(10): 2093-2110
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v15/i10/2093.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v15.i10.2093