Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Diabetes. Oct 15, 2024; 15(10): 2081-2092
Published online Oct 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i10.2081
Published online Oct 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i10.2081
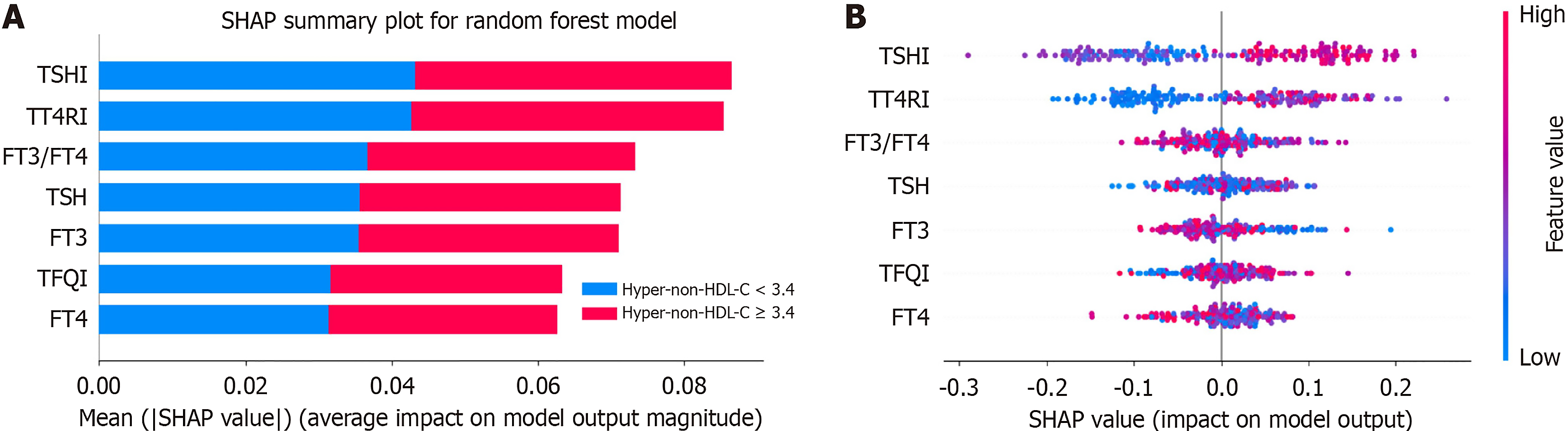
Figure 3 Feature importance of Shapley Additive Explanations values for the random forest model in detecting hyper-non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol.
A: Variables with the most significant impact on the prediction of hyper-non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (hyper-non-HDL-C) ranked in order of importance; B: Distribution of the influence of each variable on the prediction of hyper-non-HDL-C. The numerical characteristics of the variables are visually represented by colors, with larger values shown in red and smaller values shown in blue. Negative Shapley Additive Explanations values (spread to the left) suggest a decrease in the probability of hyper-non-HDL-C, whereas positive values (spread to the right) suggest an increase in probability. SHAP: Shapley Additive Explanations; FT3: Free triiodothyronine; FT4: Free thyrotropin; TSH: Thyroid-stimulating hormone; TSHI: Thyroid-stimulating hormone index; TT4RI: Thyrotrophic T4 resistance index; TFQI: Thyroid feedback quantile-based index; Hyper-non-HDL-C: Non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol.
- Citation: Duan XY, Fu JL, Sun LN, Mu ZJ, Xiu SL. Association between sensitivity to thyroid hormones and non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. World J Diabetes 2024; 15(10): 2081-2092
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v15/i10/2081.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v15.i10.2081