Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Diabetes. Jan 15, 2024; 15(1): 53-71
Published online Jan 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i1.53
Published online Jan 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i1.53
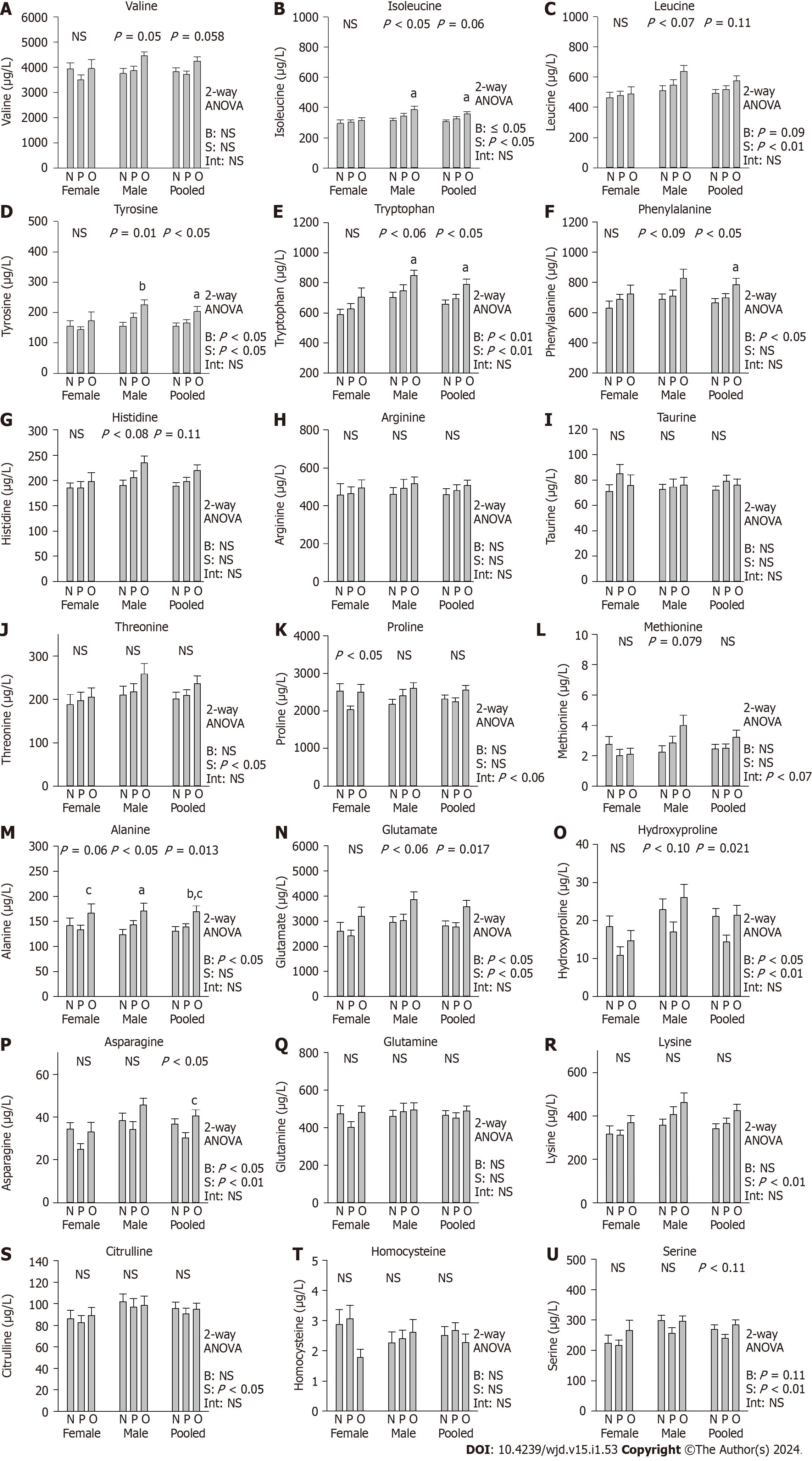
Figure 1 One-way and two-way ANOVA of the effects of body mass index and sex on serum amino acid concentrations in male and female new-onset type-2 diabetes patients in differing body mass index categories.
A: Valine; B: Isoleucine; C: Leucine; D: Tyrosine; E: Tryptophan; F: Phenylalanine; G: Histidine; H: Arginine; I: Taurine; J: Threonine; K: Proline; L: Methionine; M: Alanine; N: Glutamate; O: Hydroxyproline; P: Asparagine; Q: Glutamine; R: Lysine; S: Citrulline; T: Homocysteine; U: Serine. N: Normal weight; P: Overweight; O: Obese group. aP < 0.05 vs normal weight; bP < 0.01 vs normal weight; cP < 0.05 vs overweight; NS: Not significantly different (P > 0.05); B: Body mass index; S: Sex/sex; Int: BMI × sex interaction.
- Citation: Wang M, Ou Y, Yuan XL, Zhu XF, Niu B, Kang Z, Zhang B, Ahmed A, Xing GQ, Su H. Heterogeneously elevated branched-chain/aromatic amino acids among new-onset type-2 diabetes mellitus patients are potentially skewed diabetes predictors. World J Diabetes 2024; 15(1): 53-71
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v15/i1/53.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v15.i1.53