Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Diabetes. Sep 15, 2023; 14(9): 1349-1368
Published online Sep 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i9.1349
Published online Sep 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i9.1349
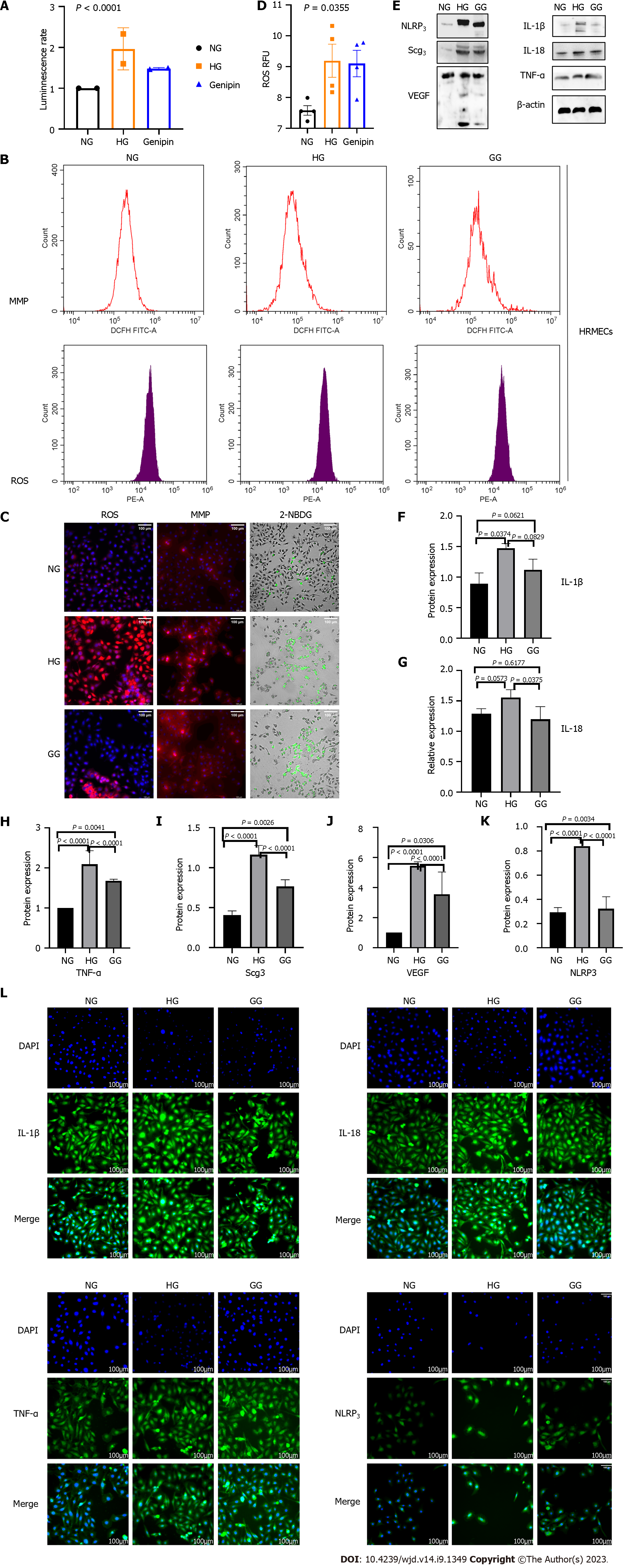
Figure 3 Genipin protects human retinal microvascular endothelial cells from high glucose damage with regard to energy metabolism, oxidative stress, and inflammatory injury in vitro.
A: ATP levels among normal glucose, high glucose, and genipin-treated human retinal microvascular endothelial cells (hRMECs); B-D: Reactive oxygen species, mitochondrial membrane potential, and 2-[N-(7-nitrobenz-2-oxa-1,3-diazol-4-yl) amino]-2-deoxy-d-glucose levels in hRMECs treated with high glucose and genipin; E-L: Western blot and immunofluorescence to measure the expression of inflammatory factors expression. IL: Interleukin; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha; NLRP3: Nucleotide-binding domain, leucine-rich-containing family, pyrin domain-containing 3; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; MMP: Mitochondrial membrane potential; 2-NBDG: 2-[N-(7-nitrobenz-2-oxa-1,3-diazol-4-yl) amino]-2-deoxy-d-glucose; hRMECs: Human retinal microvascular endothelial cells. NG: 5 mmol/L glucose containing ECM-treated hRMECs group; HG: 30 mmol/L glucose containing ECM-treated hRMECs group; GG: 0.4 μM genipin + 30 mmol/L glucose containing ECM-treated hRMECs.
- Citation: Sun KX, Chen YY, Li Z, Zheng SJ, Wan WJ, Ji Y, Hu K. Genipin relieves diabetic retinopathy by down-regulation of advanced glycation end products via the mitochondrial metabolism related signaling pathway. World J Diabetes 2023; 14(9): 1349-1368
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v14/i9/1349.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v14.i9.1349