Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Diabetes. Jul 15, 2023; 14(7): 1013-1026
Published online Jul 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i7.1013
Published online Jul 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i7.1013
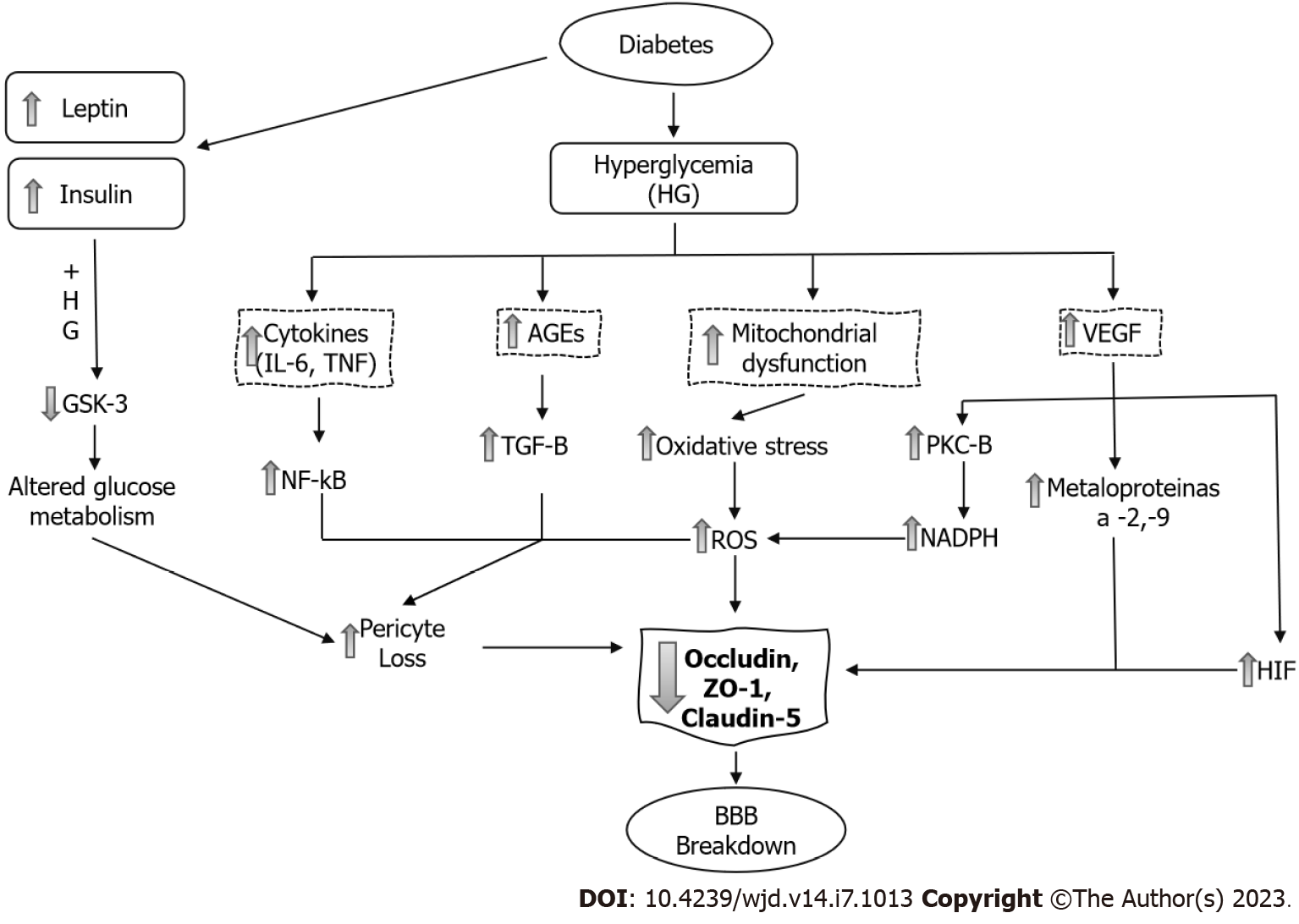
Figure 3 Mechanisms of blood-brain-barrier dysfunction in diabetes mellitus.
AGE: Advanced glycation end-product; BBB: Blood-brain-barrier; GSK-3: Glycogen synthase kinase 3; HG: Hyperglycemia; HIF: Hypoxia-inducible factor; IL-6: Interleukin 6; NADPH: Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; NF-κB: Nuclear factor-kappa B; PKC-B: Protein kinase C; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; TGF-β: Transforming growth factor; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; ZO-1: Zonula occludens.
- Citation: Robles-Osorio ML, Sabath E. Tight junction disruption and the pathogenesis of the chronic complications of diabetes mellitus: A narrative review. World J Diabetes 2023; 14(7): 1013-1026
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v14/i7/1013.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v14.i7.1013