Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Diabetes. Jun 15, 2023; 14(6): 724-740
Published online Jun 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i6.724
Published online Jun 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i6.724
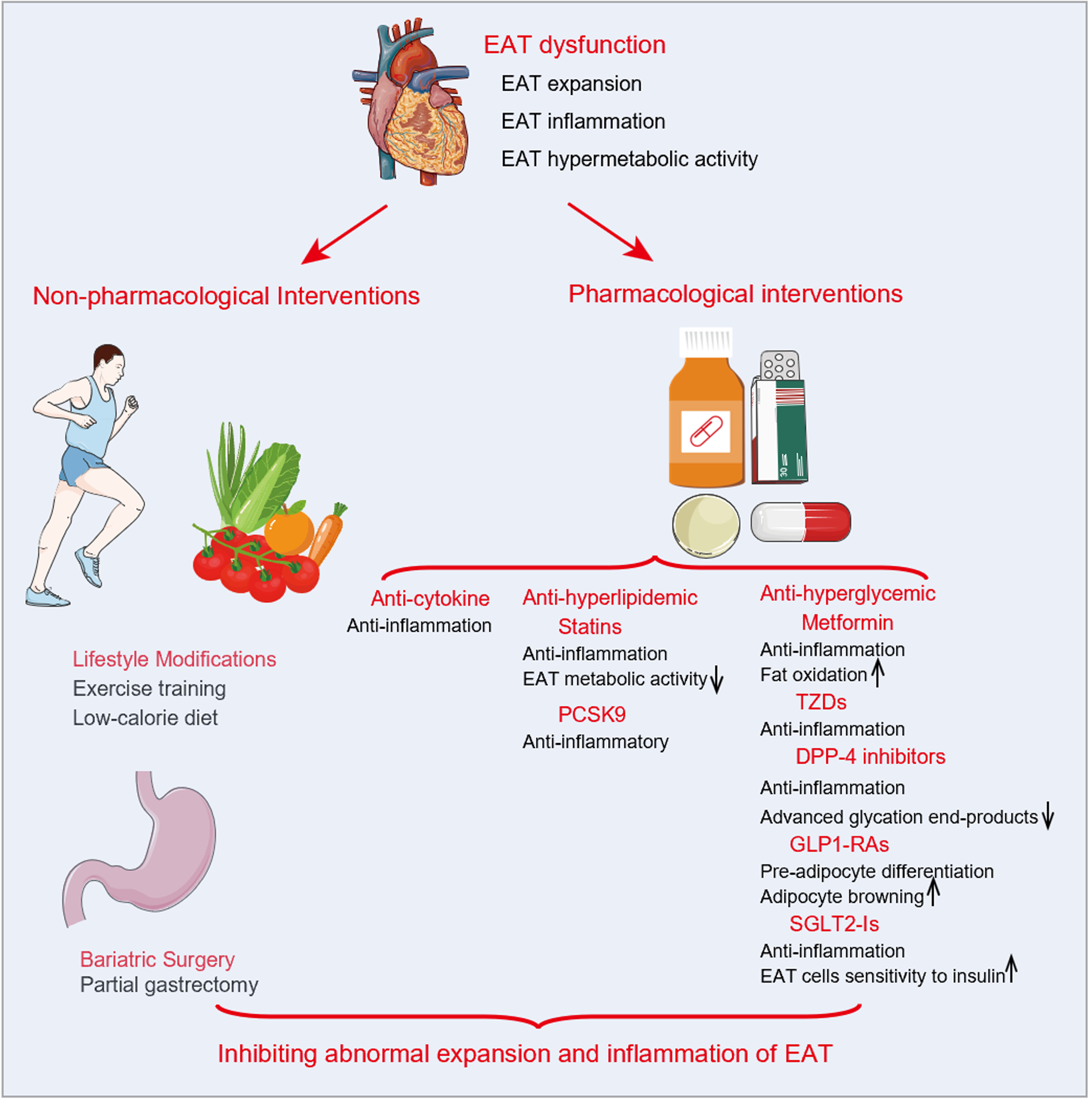
Figure 3 Current interventions targeting epicardial adipose tissue and possible mechanisms.
Current interventions targeting epicardial adipose tissue (EAT) reported in the literature include non-pharmacological interventions (lifestyle management and bariatric surgery) and pharmacological interventions related to anti-cytokines, anti-hyperlipidemia, and anti-hyperglycemia. By increasing fat oxidation or sensitivity to insulin and inhibiting inflammation or hypermetabolic activity, these interventions may prevent abnormal expansion and inflammation of EAT. EAT: Epicardial adipose tissue; DPP-4: Dipeptidyl peptidase 4; GLP1-RAs: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists; PCSK9: Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9; SGLT2-Is: Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors; TZDs: Thiazolidinediones.
- Citation: Shi YJ, Dong GJ, Guo M. Targeting epicardial adipose tissue: A potential therapeutic strategy for heart failure with preserved ejection fraction with type 2 diabetes mellitus. World J Diabetes 2023; 14(6): 724-740
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v14/i6/724.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v14.i6.724