Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Diabetes. May 15, 2023; 14(5): 549-559
Published online May 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i5.549
Published online May 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i5.549
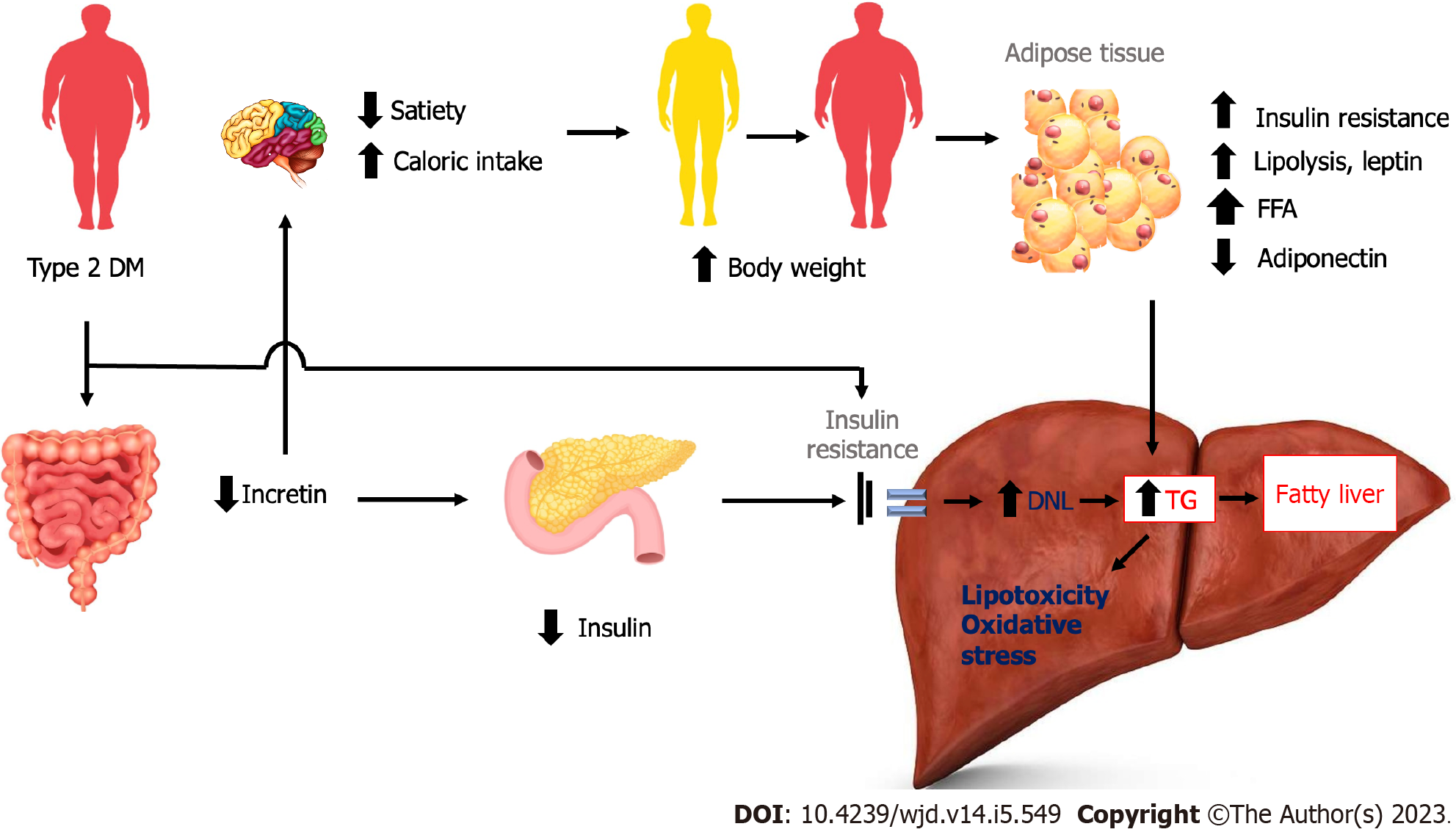
Figure 3 The effect of type 2 diabetes mellitus on incretin hormone and the development of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Increased body weight as the result of reduced incretin effects leads to adipose tissue insulin resistance, increased lipolysis and leptin, and decreased adiponectin, resulting in hepatic fat deposition. DM: Diabetes Mellitus; DNL: De novo lipogenesis; FFA: Free fatty acids; TG: Triglycerides.
- Citation: Wibawa IDN, Mariadi IK, Somayana G, Krisnawardani Kumbara CIY, Sindhughosa DA. Diabetes and fatty liver: Involvement of incretin and its benefit for fatty liver management. World J Diabetes 2023; 14(5): 549-559
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v14/i5/549.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v14.i5.549