Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Diabetes. May 15, 2023; 14(5): 494-511
Published online May 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i5.494
Published online May 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i5.494
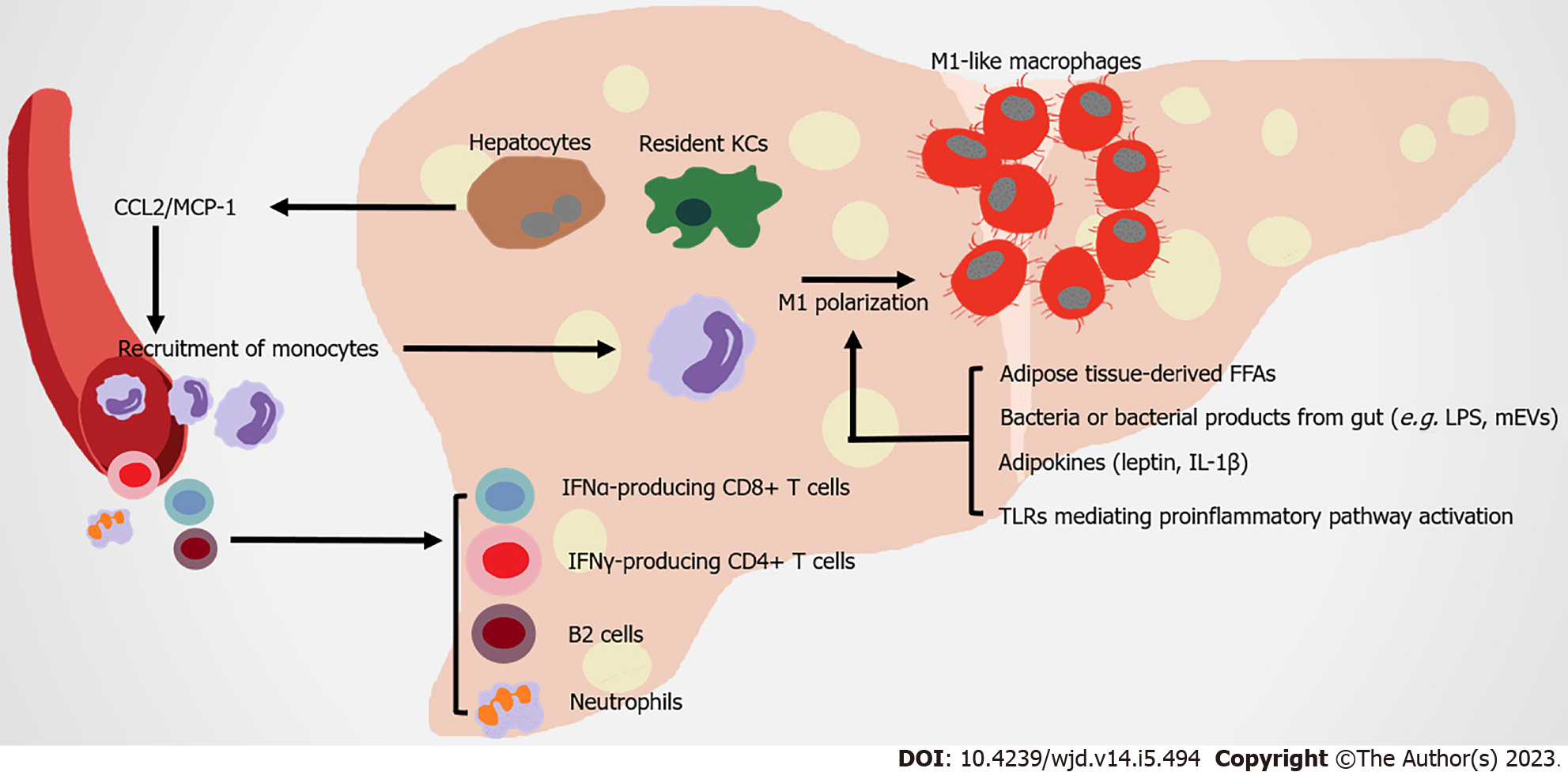
Figure 3 Immune attack and inflammation in the liver in obesity-related type 2 diabetes.
Under metabolic stress, recruited hepatic macrophages, which are derived from circulating monocytes, are recruited by steatosis hepatocytes and Kupffer cells secreting monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP1). Expanded adipose tissue-derived free fatty acids, leptin, interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β) and bacteria with their products from gut, contribute to the M1 polarization of hepatic macrophages. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) is a severe form of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, which is associated with more severe hepatic insulin resistance and inflammation. The infiltration of neutrophils, B2 cells, interferon gamma (IFN-γ)-producing CD4+ T cells and IFN-α-producing CD8+ T cells occur in NASH liver, promoting insulin resistance under diet-induced metabolic stress. FFAs: Free fatty acids; KCs: Kupffer cells; LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; mEVs: Extracellular vesicles.
- Citation: Wang HW, Tang J, Sun L, Li Z, Deng M, Dai Z. Mechanism of immune attack in the progression of obesity-related type 2 diabetes. World J Diabetes 2023; 14(5): 494-511
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v14/i5/494.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v14.i5.494