Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Diabetes. Mar 15, 2023; 14(3): 234-254
Published online Mar 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i3.234
Published online Mar 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i3.234
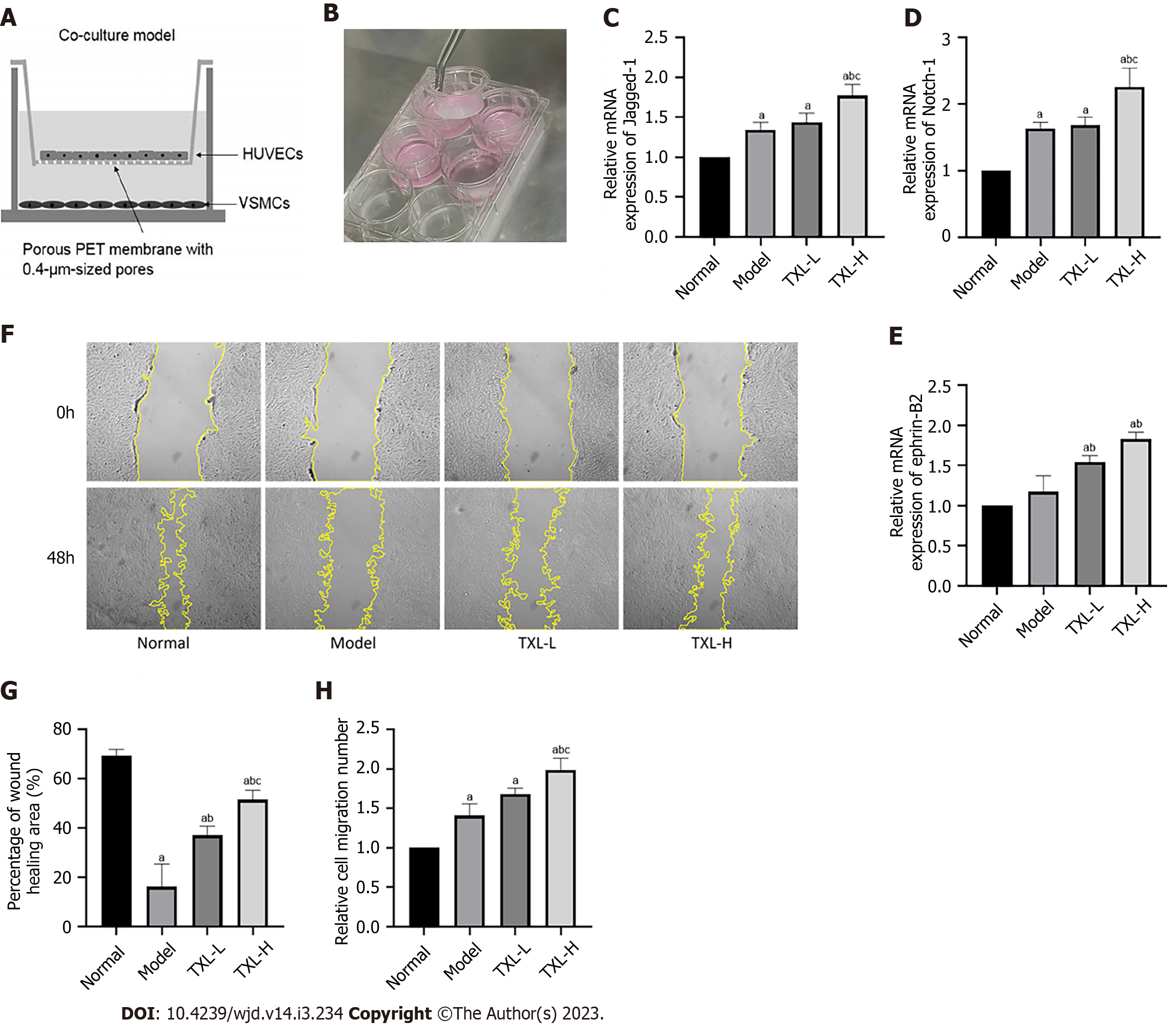
Figure 8 Tongxinluo enhanced the interaction between human vascular endothelial cells and vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) and promoted the migration of VSMCs.
A and B: Schematic diagram and photos of the coculture system; C-E: Quantitative analysis of Jagged-1, Ntoch-1 and ephrin-B2 mRNA expression was determined via RT-PCR; F: Scratch assay to detect VSMC migration ability. G: Percentage of the wound healing area was measured using ImageJ software; H: Transwell assays were performed to detect VSMC migration ability and the relative cell migration number was calculated by ImageJ software. The values are shown as the means ± SDs. aP < 0.05 compared with the normal group, bP <0.05 compared with the model group, cP < 0.05 compared with the TXL-L group, n = 3. TXL: Tongxinluo; HUVECs: Human vascular endothelial cells; VSMCs: Vascular smooth muscle cells.
- Citation: Gu JJ, Hou YL, Yan YH, Li J, Wei YR, Ma K, Wang XQ, Zhang JH, Wang DD, Li CR, Li DQ, Sun LL, Gao HL. Tongxinluo promotes endothelium-dependent arteriogenesis to attenuate diabetic peripheral arterial disease. World J Diabetes 2023; 14(3): 234-254
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v14/i3/234.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v14.i3.234