Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Diabetes. Mar 15, 2023; 14(3): 209-221
Published online Mar 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i3.209
Published online Mar 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i3.209
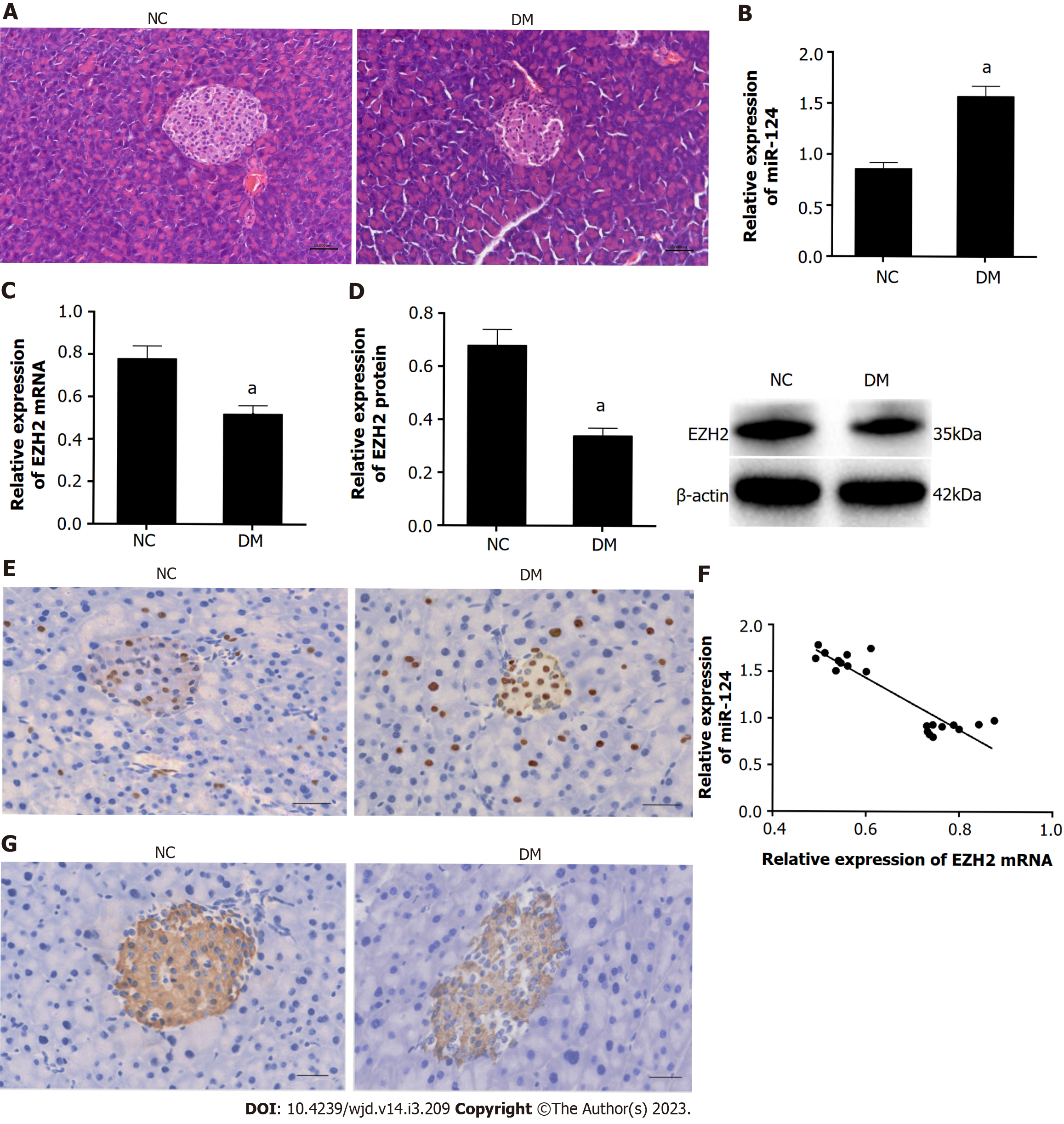
Figure 1 miR-124 was upregulated and EZH2 was downregulated in pancreatic tissue in diabetic mice.
A: The pathological changes of pancreas in diabetic mice detected by hematoxylin-eosin staining (scale bar = 50 μm); B: The relative expression levels of miR-124 in pancreatic tissue of diabetic mice were higher than that of the normal control (NC) mice detected by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR); C and D: The relative expression levels of EZH2 in pancreatic tissues of diabetic mice were lower than that of NC mice detected by RT-qPCR and western blot; E: Expression of EZH2 in pancreatic tissue was detected by immunohistochemistry (scale bar = 100 μm); F: miR-124 was negatively correlated with EZH2 analyzed by Pearson correlation analysis; G: Expression of insulin in pancreatic tissue was detected by immunohistochemistry (scale bar = 100 μm). aP < 0.05, vs the NC group. NC: Normal control; DM: Diabetes group.
- Citation: Duan XK, Sun YX, Wang HY, Xu YY, Fan SZ, Tian JY, Yu Y, Zhao YY, Jiang YL. miR-124 is upregulated in diabetic mice and inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis of high-glucose-induced β-cells by targeting EZH2. World J Diabetes 2023; 14(3): 209-221
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v14/i3/209.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v14.i3.209