Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Diabetes. Mar 15, 2023; 14(3): 159-169
Published online Mar 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i3.159
Published online Mar 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i3.159
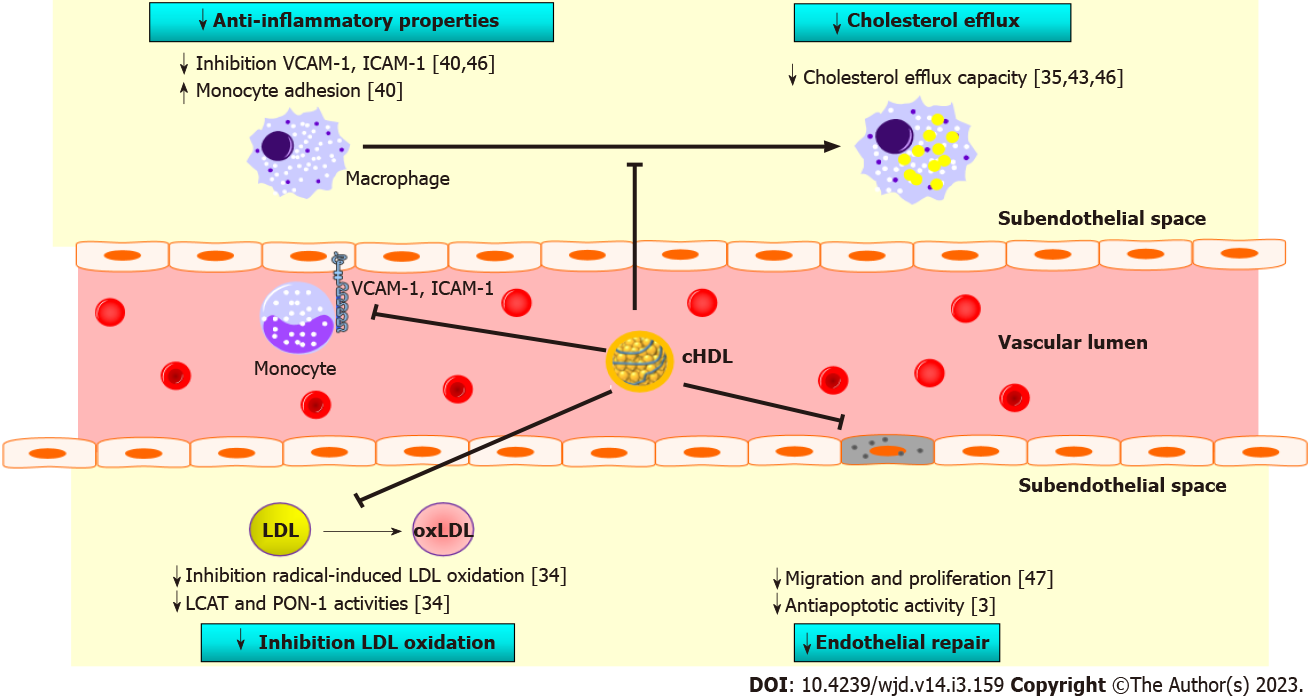
Figure 3 Role of carbamylated high-density lipoproteins in atherosclerosis.
The atheroprotective properties of high-density lipoproteins (HDL) are altered after carbamylation. Thus, carbamylation HDL (cHDL) partially loses its ability to remove cholesterol from macrophages and to inhibit monocyte adhesion. cHDL is less able to protect low-density lipoproteins from oxidation, likely due to reduced lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase and paraoxonase-1 activities. Lastly, cHDL has an impaired capacity to facilitate endothelial repair. VCAM-1: Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1; ICAM-1: Intercellular adhesion molecule-1; PAI-1: Plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1; LDL: Low-density lipoproteins; LCAT: Lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase; PON-1: Paraoxonase-1; cHDL: Carbamylation high-density lipoproteins.
- Citation: Denimal D. Carbamylated lipoproteins in diabetes. World J Diabetes 2023; 14(3): 159-169
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v14/i3/159.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v14.i3.159