Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Diabetes. Mar 15, 2023; 14(3): 159-169
Published online Mar 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i3.159
Published online Mar 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i3.159
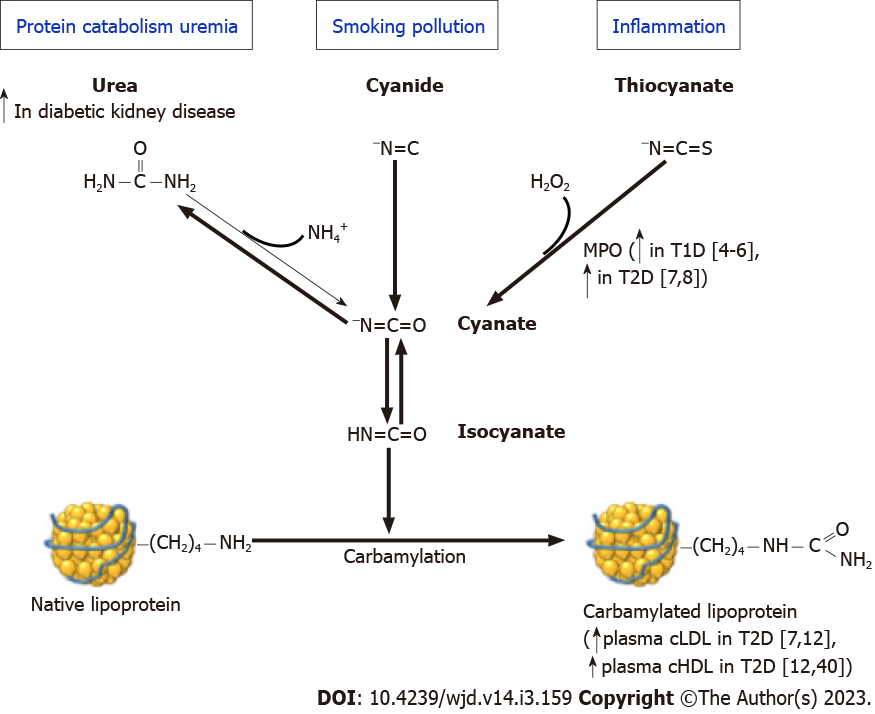
Figure 1 Carbamylation of lipoproteins is a non-enzymatic irreversible process mediated by isocyanate, and corresponds to the irreversible binding of a carbamoyl moiety to ε-NH2 of lysine residues in proteins, resulting in carbamyllysine.
Isocyanate originates from either the non-enzymatic spontaneous dissociation of urea, or from the myeloperoxidase (MPO)-mediated oxidation of thiocyanate, or to a lesser extent from tobacco smoke or atmospheric pollution. The urea pathway is of particular relevance in diabetic patients with chronic kidney disease. MPO level is elevated in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes (T2D). Plasma levels of carbamylated low-density lipoproteins and high-density lipoproteins are increased in T2D patients with or without chronic kidney disease. T2D: Type 2 diabete; CML: Carbamyllysine; MPO: Myeloperoxidase; Lys: Lysine; cLDL: Carbamylated low-density lipoproteins; cHDL: Carbamylated high-density lipoproteins.
- Citation: Denimal D. Carbamylated lipoproteins in diabetes. World J Diabetes 2023; 14(3): 159-169
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v14/i3/159.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v14.i3.159