Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Diabetes. Mar 15, 2023; 14(3): 130-146
Published online Mar 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i3.130
Published online Mar 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i3.130
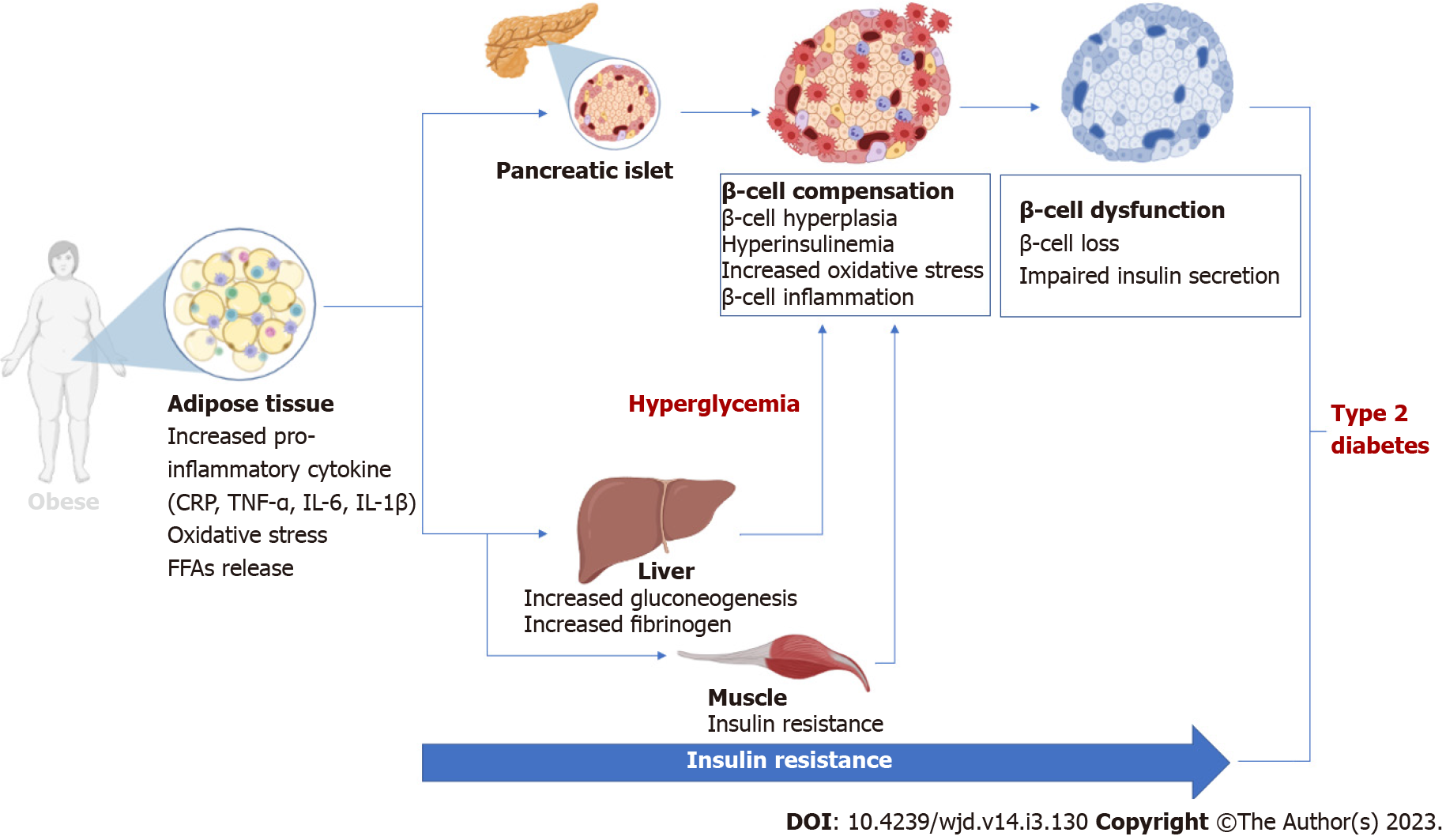
Figure 1 An overview of the pathological implications of adipose tissue hypertrophy and insulin resistance during the development and progressive loss of β-cell function in conditions of obesity to type 2 diabetes.
Briefly, adipose tissue expansion (usually seen in obesity or type 2 diabetes) is associated with enhanced secretion of pro-inflammatory markers and generation of oxidative stress that directly or indirectly cause pancreatic β-cell loss, leading to impaired insulin secretion. CRP: C-reactive protein; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha; IL: Interleukin; FFAs: Free fatty acids.
- Citation: Dludla PV, Mabhida SE, Ziqubu K, Nkambule BB, Mazibuko-Mbeje SE, Hanser S, Basson AK, Pheiffer C, Kengne AP. Pancreatic β-cell dysfunction in type 2 diabetes: Implications of inflammation and oxidative stress. World J Diabetes 2023; 14(3): 130-146
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v14/i3/130.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v14.i3.130