Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Diabetes. Feb 15, 2023; 14(2): 76-91
Published online Feb 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i2.76
Published online Feb 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i2.76
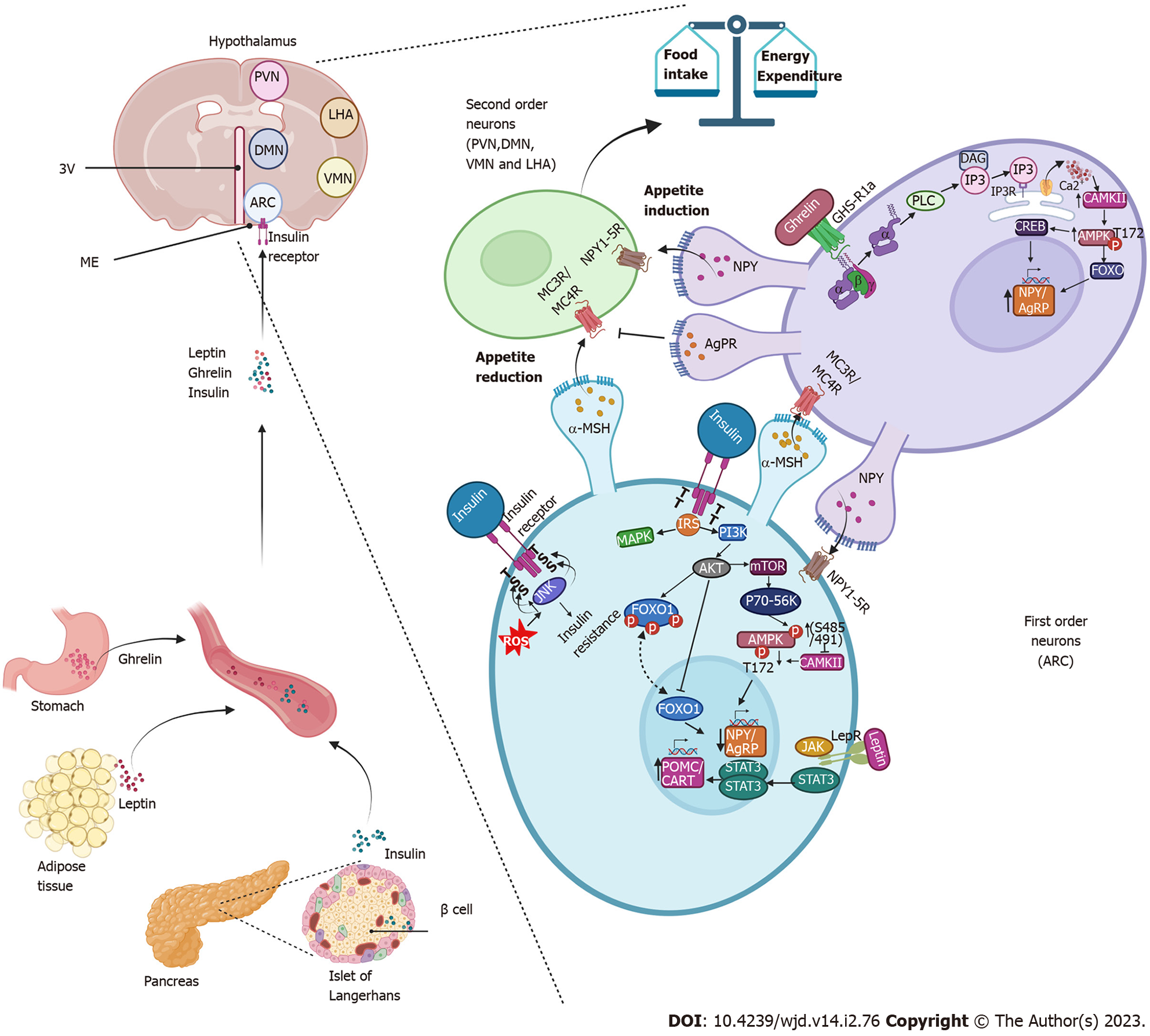
Figure 4 Insulin promotes decreased appetite in the arcuate nucleus.
Insulin is secreted by the cells of the pancreas and through the circulation reaches the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus. It binds to its receptor on first-order neurons, triggering the phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase/protein kinase B signaling pathways and forkhead box protein O1 repression, resulting in decreased expression of neuropeptide Y (NPY) and agouti-related protein resulting in an anorexigenic effect. Like insulin, leptin activates anorexigenic signaling pathways by binding to its receptor, which activates the Janus tyrosine kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription pathway, promoting the expression of the anorexigenic peptide precursor neuropeptide of α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone and transcript regulated by cocaine and amphetamines and with it the release of the α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone that activates the melanocortin receptors (MC3R/MC4R) in the neurons of the second order. Together, insulin and leptin signals amplify the anorexigenic effect. During fasting periods, ghrelin activates the growth hormone receptor 1a and promotes the activation of the adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase pathway that promotes the expression of NPY/agouti-related protein, stimulates orexigenic receptor Gi-coupled NPY in second-order neurons and prevents α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone from binding to melanocortin receptors (MC3R/MC4R), driving the orexigenic signal. 3V: Third ventricle; DAG: Diacylglycerol; IP3: Inositol triphosphate; IP3R: Inositol triphosphate receptor; ME: Median eminence; PLC: Phospholipase C; ROS: Reactive oxygen species.
- Citation: De la Cruz-Concepción B, Flores-Cortez YA, Barragán-Bonilla MI, Mendoza-Bello JM, Espinoza-Rojo M. Insulin: A connection between pancreatic β cells and the hypothalamus. World J Diabetes 2023; 14(2): 76-91
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v14/i2/76.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v14.i2.76