Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Diabetes. Dec 15, 2023; 14(12): 1862-1876
Published online Dec 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i12.1862
Published online Dec 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i12.1862
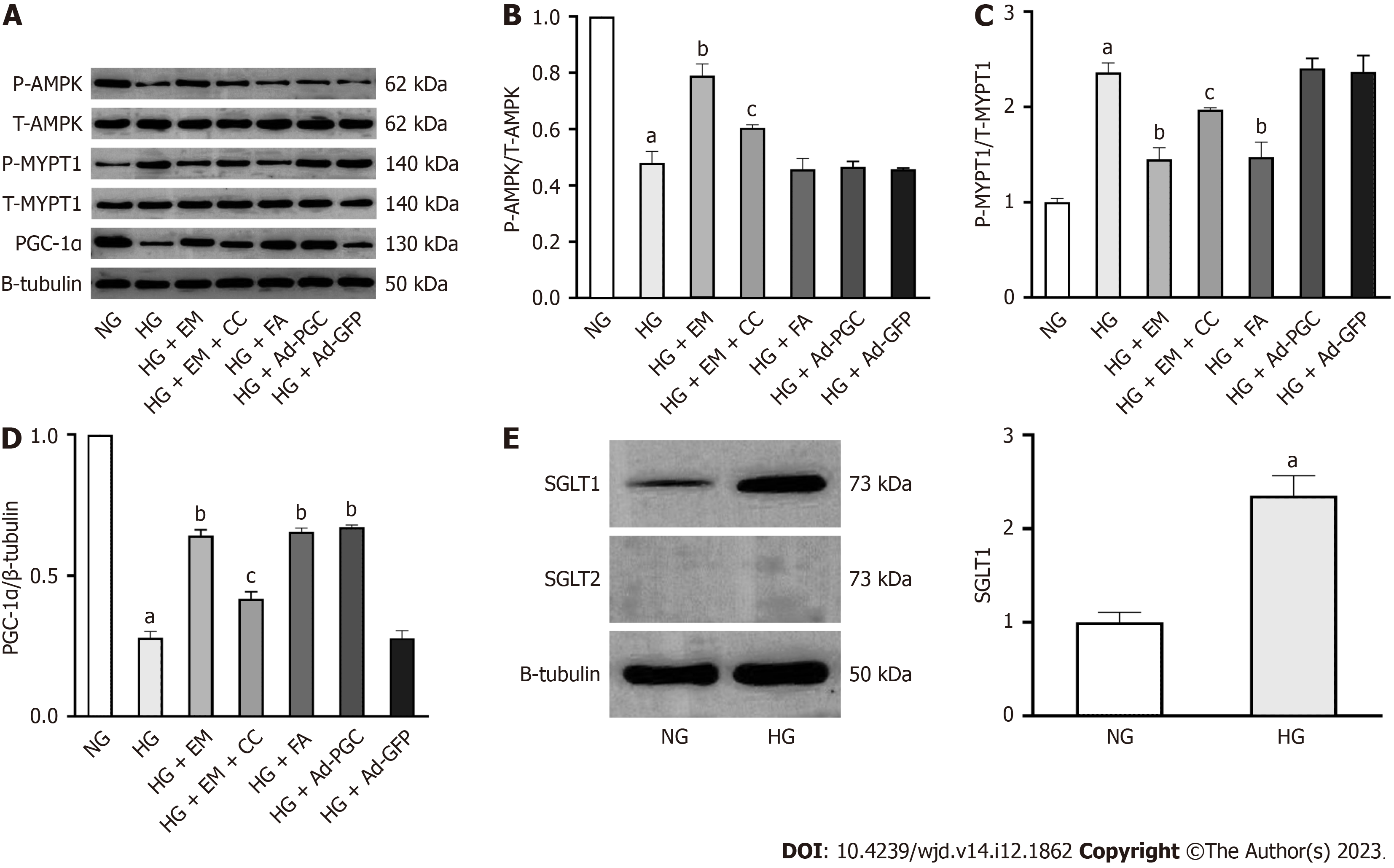
Figure 6 Relationship of empagliflozin with AMP-activated protein kinase, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator-1α, and the RhoA/ROCK pathway in cardiomyocytes in HG conditions in vitro.
A-D: The phosphorylation of AMP-activated protein kinase and myosin phosphatase target subunit 1, as well as the protein expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator-1α were measured by Western blot in three groups; E: Sodium-glucose cotransporter (SGLT)1 and SGLT2 protein expression in cardiomyocytes. Bars indicate the mean ± SD from three independent experiments (n = 3). β-tubulin was set as a control for normalization. NG: Normal glucose; HG: High glucose; EM: Empagliflozin; CC: Compound C; FA: Fasudil; HG + Ad–PGC: Cells were transfected with PGC-1α-GFP-Ad. aP < 0.05 vs NG; bP < 0.05 vs HG; cP < 0.05 vs HG + EM.
- Citation: Li N, Zhu QX, Li GZ, Wang T, Zhou H. Empagliflozin ameliorates diabetic cardiomyopathy probably via activating AMPK/PGC-1α and inhibiting the RhoA/ROCK pathway. World J Diabetes 2023; 14(12): 1862-1876
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v14/i12/1862.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v14.i12.1862