Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Diabetes. Dec 15, 2023; 14(12): 1862-1876
Published online Dec 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i12.1862
Published online Dec 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i12.1862
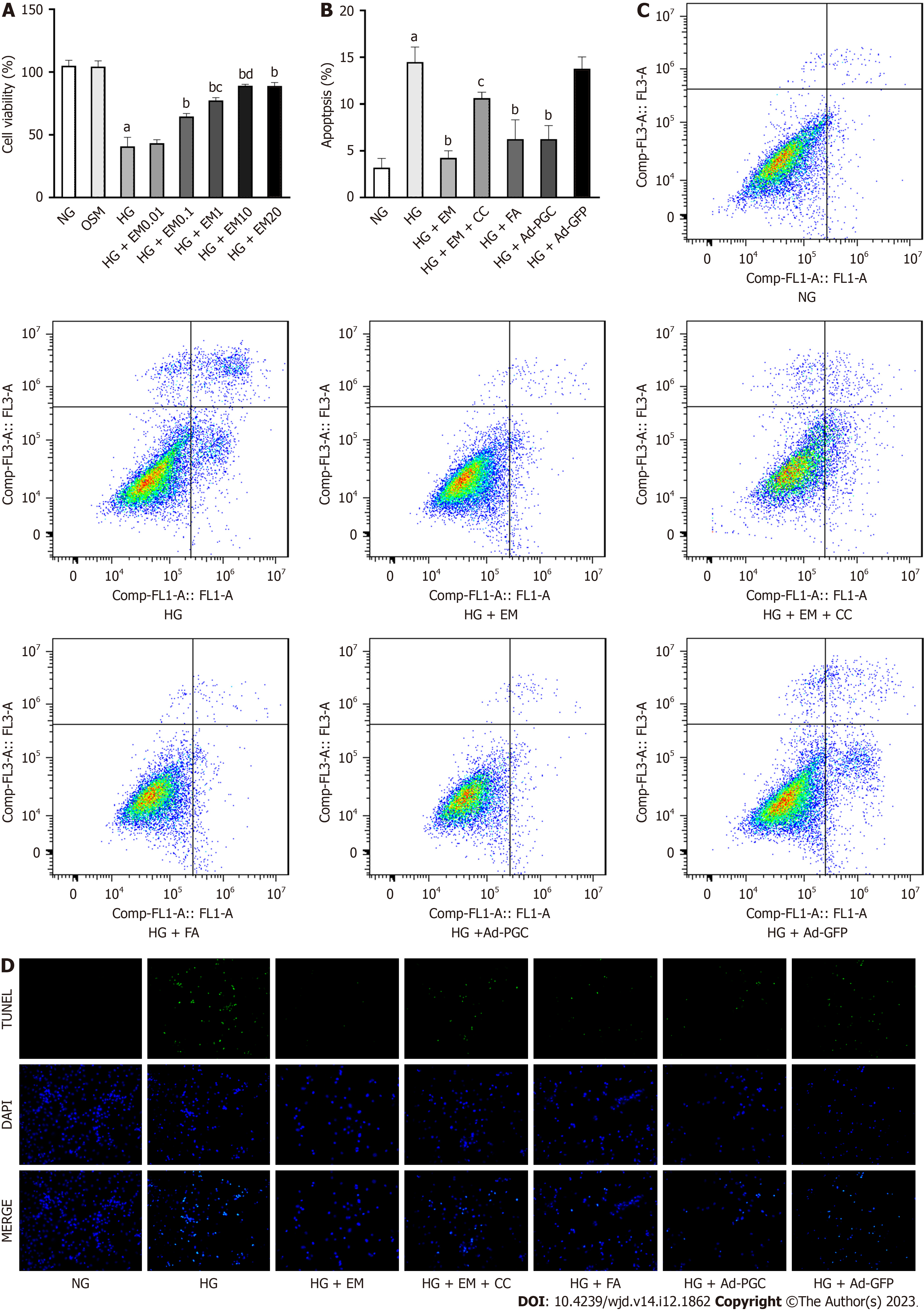
Figure 3 Effects of empagliflozin, fasudil, and overexpression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator-1α on high glucose-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis in vitro.
A: Effects of different concentrations of empagliflozin on viability of cardiomyocytes exposed to high glucose (HG); B and C: Cardiomyocyte apoptosis measured by flow cytometry; D: TdT-mediated dUTP-biotin nick end labeling staining of cardiomyocytes in each group. Bars indicate the mean ± SD from three independent experiments (n = 3). NG: Normal glucose; HG: High glucose; EM: Empagliflozin; CC: Compound C; FA: Fasudil; HG + Ad–PGC: Cells were transfected with peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator-1α-GFP-Ad; HG + Ad-GFP: Cells transfected with GFP-Ad. aP < 0.05 vs NG; bP < 0.05 vs HG; cP < 0.05 vs HG + EM.
- Citation: Li N, Zhu QX, Li GZ, Wang T, Zhou H. Empagliflozin ameliorates diabetic cardiomyopathy probably via activating AMPK/PGC-1α and inhibiting the RhoA/ROCK pathway. World J Diabetes 2023; 14(12): 1862-1876
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v14/i12/1862.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v14.i12.1862