Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Diabetes. Dec 15, 2023; 14(12): 1824-1838
Published online Dec 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i12.1824
Published online Dec 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i12.1824
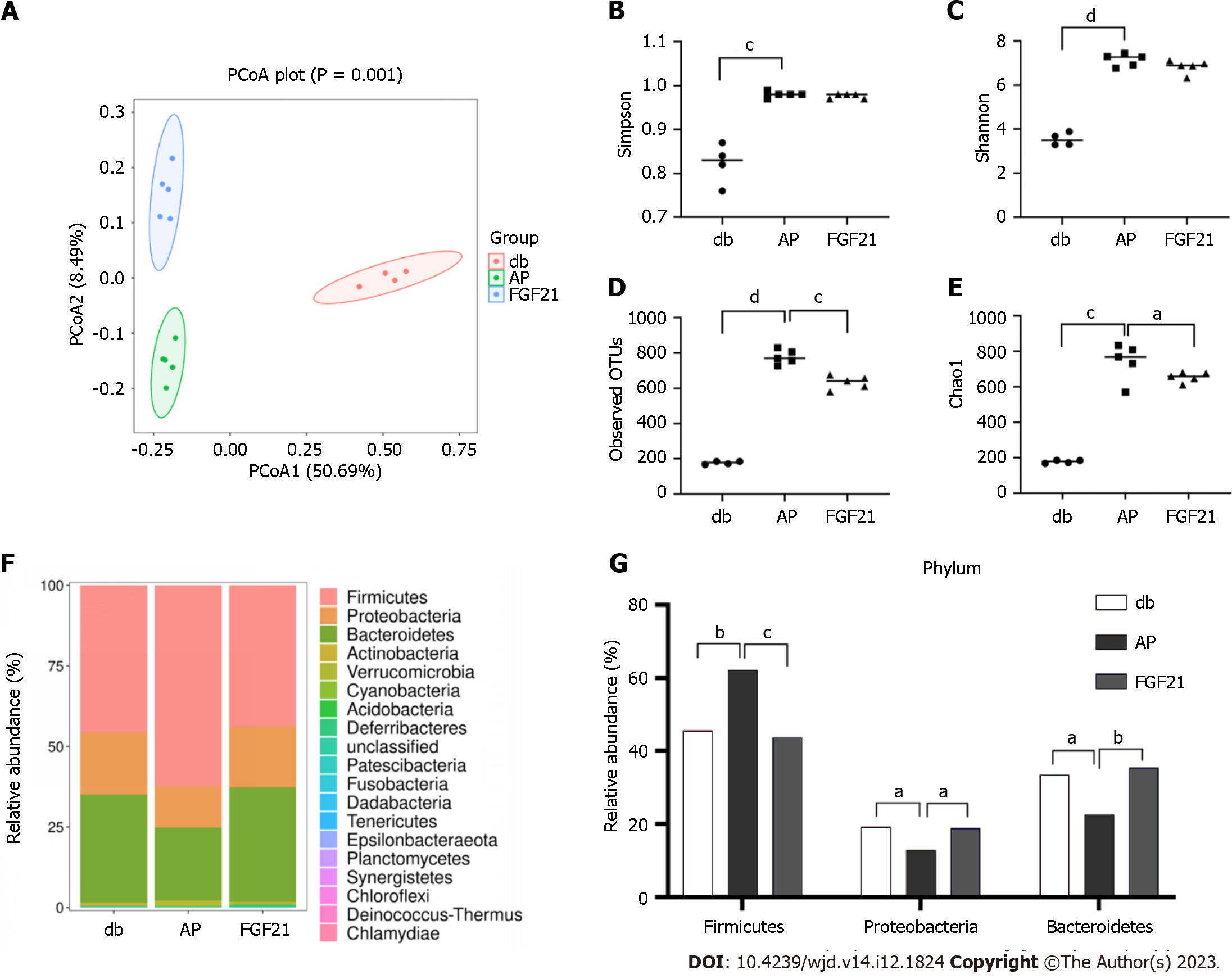
Figure 3 Fibroblast growth factor 21 treatment improves the composition of gut microbiota.
A: Principal coordinate analysis results demonstrated distinct segregation of the microbial communities among the diabetic (db), acute pancreatitis (AP), and fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) groups. Different colors in the scatter plots represent samples from different groups; the higher the similarity between samples, the closer they are in the plots; B-E: The observed operational taxonomic units, Chao1, Shannon, and Simpson indices of the gut microbiota of db, AP and FGF21 group mice. All four indices increased in the AP group compared with the db group, and the FGF21 group exhibited decreases compared with the AP group; F: Bar graph of the structural distributions of fecal microbial communities at the phylum level; G: Relative abundance of the dominant phyla. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001, dP < 0.0001. AP: Acute pancreatitis; db: Diabetic; IL: Interleukin; TNF-: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha; FGF21: Fibroblast growth factor 21.
- Citation: Sun QY, Wang XY, Huang ZP, Song J, Zheng ED, Gong FH, Huang XW. Depletion of gut microbiota facilitates fibroblast growth factor 21-mediated protection against acute pancreatitis in diabetic mice. World J Diabetes 2023; 14(12): 1824-1838
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v14/i12/1824.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v14.i12.1824