Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Diabetes. Dec 15, 2023; 14(12): 1766-1783
Published online Dec 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i12.1766
Published online Dec 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i12.1766
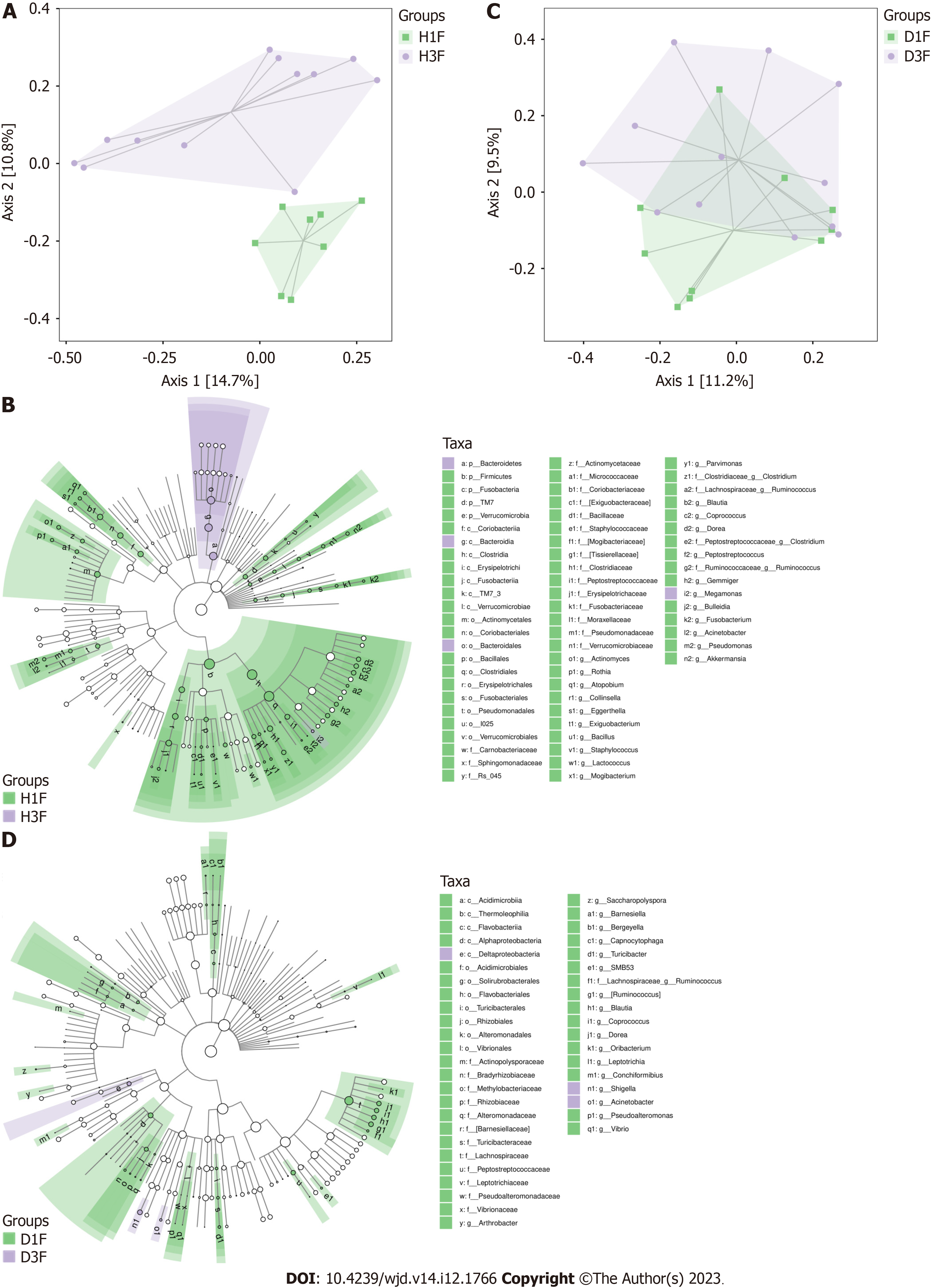
Figure 3 Comparison of gut microbiota between healthy adults and type 2 diabetes mellitus patients in the Han and Dai populations.
A: Clustering of gut microbiota composition between the healthy adults and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients in the Han population. There was a significant difference between the two groups (P < 0.05); B: Gut microbiota composition analysis between the healthy adults and T2DM patients in the Han population. There was an increased abundance of Bacteroidetes, Bacteroidales, Megamonas and Bacteroidia in the T2DM patients (P < 0.05); C: Clustering of gut microbiota composition between the healthy adults and T2DM patients in the Dai population. There were no significant differences between two groups (P > 0.05); D: Gut microbiota composition analysis between the healthy adults and T2DM patients in the Dai population. There was an increased abundance of Deltaproteobacteria, Shigella, and Acinetobacter (P < 0.05). D1F: Healthy adults in the Dai population; D3F: Type 2 diabetes mellitus patients in the Dai population; H1F: Healthy adults in the Han population; H3F: Type 2 diabetes mellitus patients in the Han population.
- Citation: Tang LT, Feng L, Cao HY, Shi R, Luo BB, Zhang YB, Liu YM, Zhang J, Li SY. Comparative study of type 2 diabetes mellitus-associated gut microbiota between the Dai and Han populations. World J Diabetes 2023; 14(12): 1766-1783
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v14/i12/1766.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v14.i12.1766