Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Diabetes. Nov 15, 2023; 14(11): 1643-1658
Published online Nov 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i11.1643
Published online Nov 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i11.1643
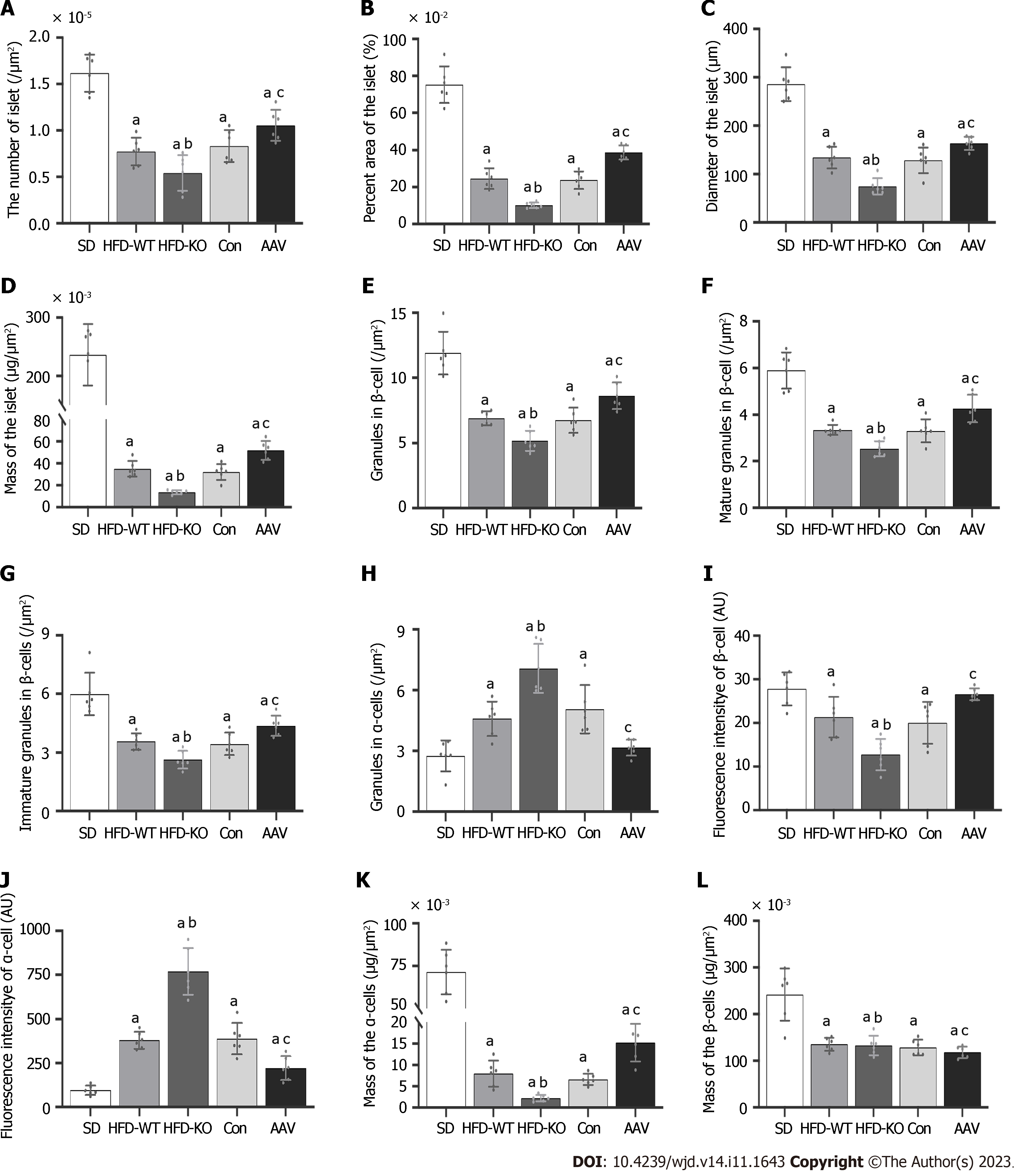
Figure 4 The quantitative analysis of vascular endothelial growth factor B affects the cellular structure of islets.
A: The number of islets; B: The relative area of the islet; C: Diameter of the islet; D: Mass of the islet; E: The number of granules in β cells; F: The number of mature granules in β cells; G: The number of immature granules in β cells; H: The number of granules in α cells; I: Mean fluorescence intensity of β cells; J: Mean fluorescence intensity of α cells; K: Mass of the β cells; L: Mass of the α cells. aP < 0.05 vs standard diet; bP < 0.05 vs high-fat diet-WT; cP < 0.05 vs Con. HFD: High-fat diet; AAV: Adeno-associated virus; SD: Standard diet.
- Citation: Li YQ, Zhang LY, Zhao YC, Xu F, Hu ZY, Wu QH, Li WH, Li YN. Vascular endothelial growth factor B improves impaired glucose tolerance through insulin-mediated inhibition of glucagon secretion. World J Diabetes 2023; 14(11): 1643-1658
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v14/i11/1643.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v14.i11.1643