Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Diabetes. Oct 15, 2023; 14(10): 1573-1584
Published online Oct 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i10.1573
Published online Oct 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i10.1573
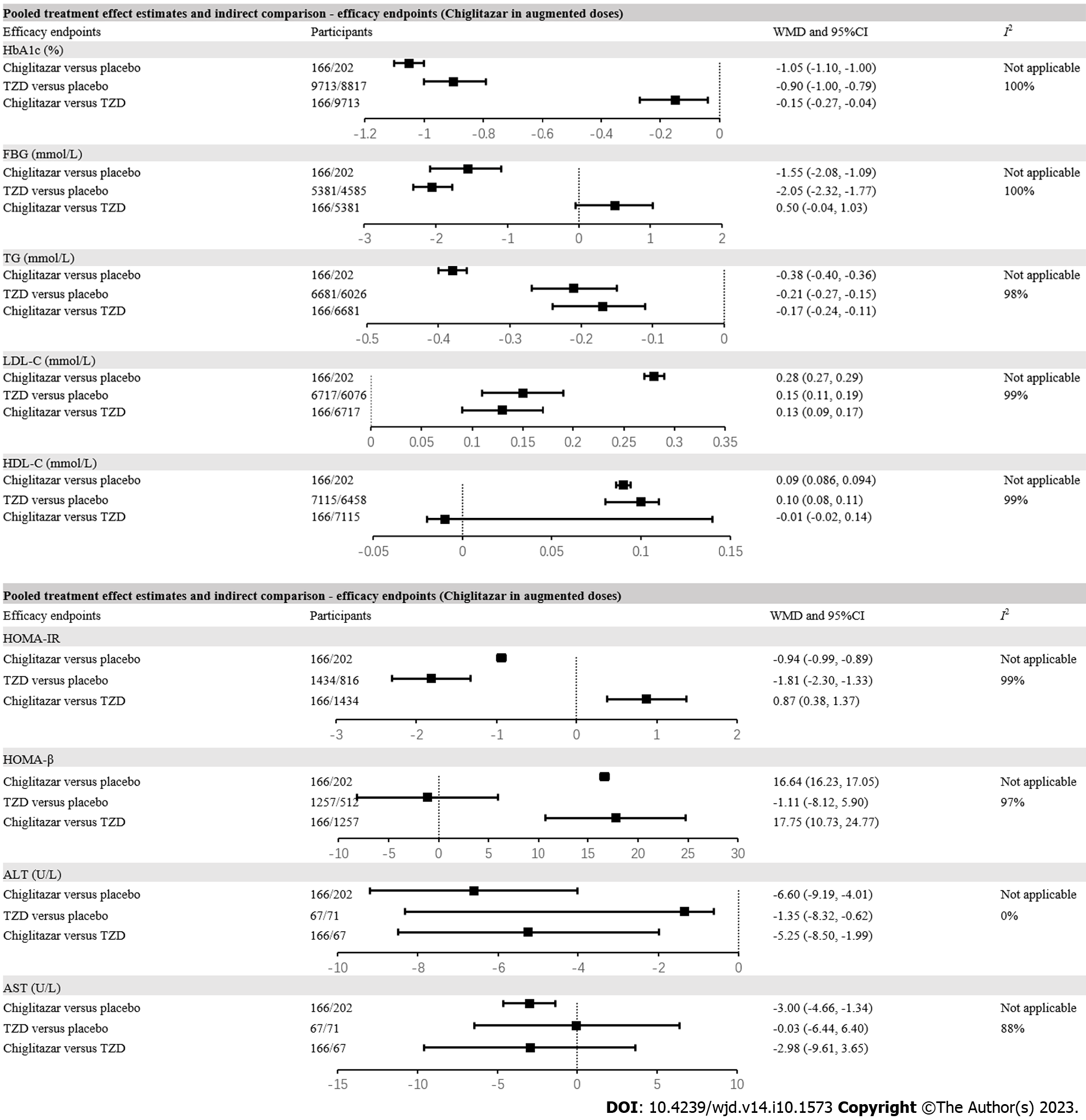
Figure 2 The forest plot exhibiting pooled effect estimates and indirect comparison between chiglitazar and thiazolidinediones on efficacy endpoints including hemoglobin A1c, fasting blood glucose, triglycerides, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance, homeostasis model assessment of β cell function, alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase.
HbA1c: Hemoglobin A1c; FBG: Fasting blood glucose; TG: Triglycerides; LDL-C: Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; HDL-C: High-density lipoprotein cholesterol; HOMA-IR: Homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance; HOMA-β: Homeostasis model assessment of β cell function; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; RR: Risk ratios; 95%CI: 95% confidential intervals; TZD: Thiazolidinedione.
- Citation: Lin C, Li ZL, Cai XL, Hu SY, Lv F, Yang WJ, Ji LN. Indirect comparison of efficacy and safety of chiglitazar and thiazolidinedione in patients with type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis. World J Diabetes 2023; 14(10): 1573-1584
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v14/i10/1573.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v14.i10.1573