Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Diabetes. May 15, 2022; 13(5): 387-407
Published online May 15, 2022. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v13.i5.387
Published online May 15, 2022. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v13.i5.387
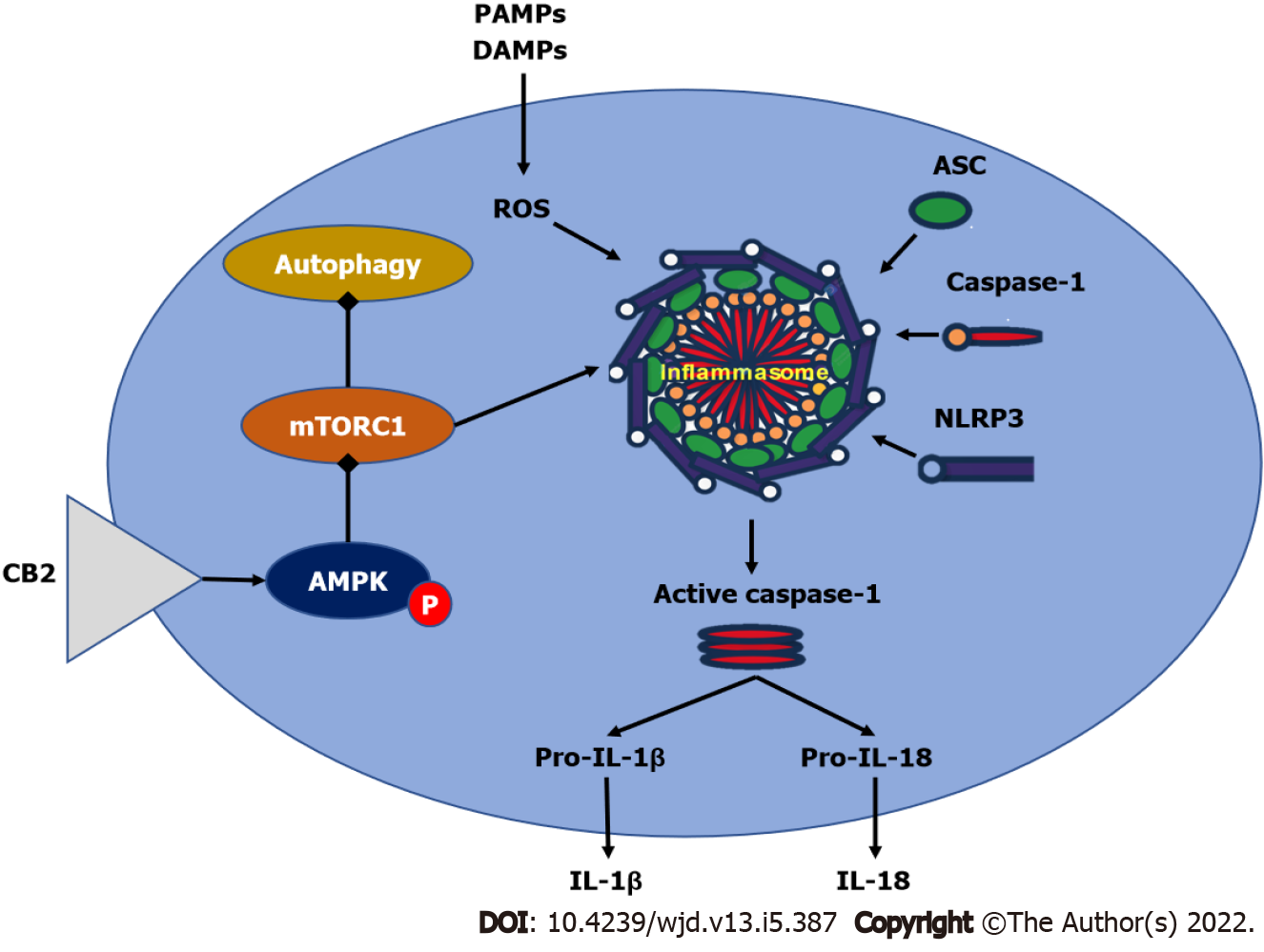
Figure 4 Effect of cannabinoid receptors on adenosine monophosphate activated protein kinase/mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1/NLR family pyrin domain containing 3 signaling.
Cannabinoids enhance the phosphorylation of adenosine monophosphate activated protein kinase (AMPK), which reduces the stimulatory effect of mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) on inflammasome assembly. Depressed activation of NLR family pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3) will diminish the activation of procaspase-1 leading to a decrease in interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and IL-18 production. Additionally, the inhibitory effect of phosphorylated AMPK on mTORC1 will enhance autophagy. AMPK: Adenosine monophosphate activated protein kinase; mTORC1: Mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1; NLRP3: NLR family pyrin domain containing 3; IL: Interleukin.
- Citation: El-Azab MF, Wakiel AE, Nafea YK, Youssef ME. Role of cannabinoids and the endocannabinoid system in modulation of diabetic cardiomyopathy. World J Diabetes 2022; 13(5): 387-407
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v13/i5/387.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v13.i5.387