Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Diabetes. Apr 15, 2022; 13(4): 319-337
Published online Apr 15, 2022. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v13.i4.319
Published online Apr 15, 2022. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v13.i4.319
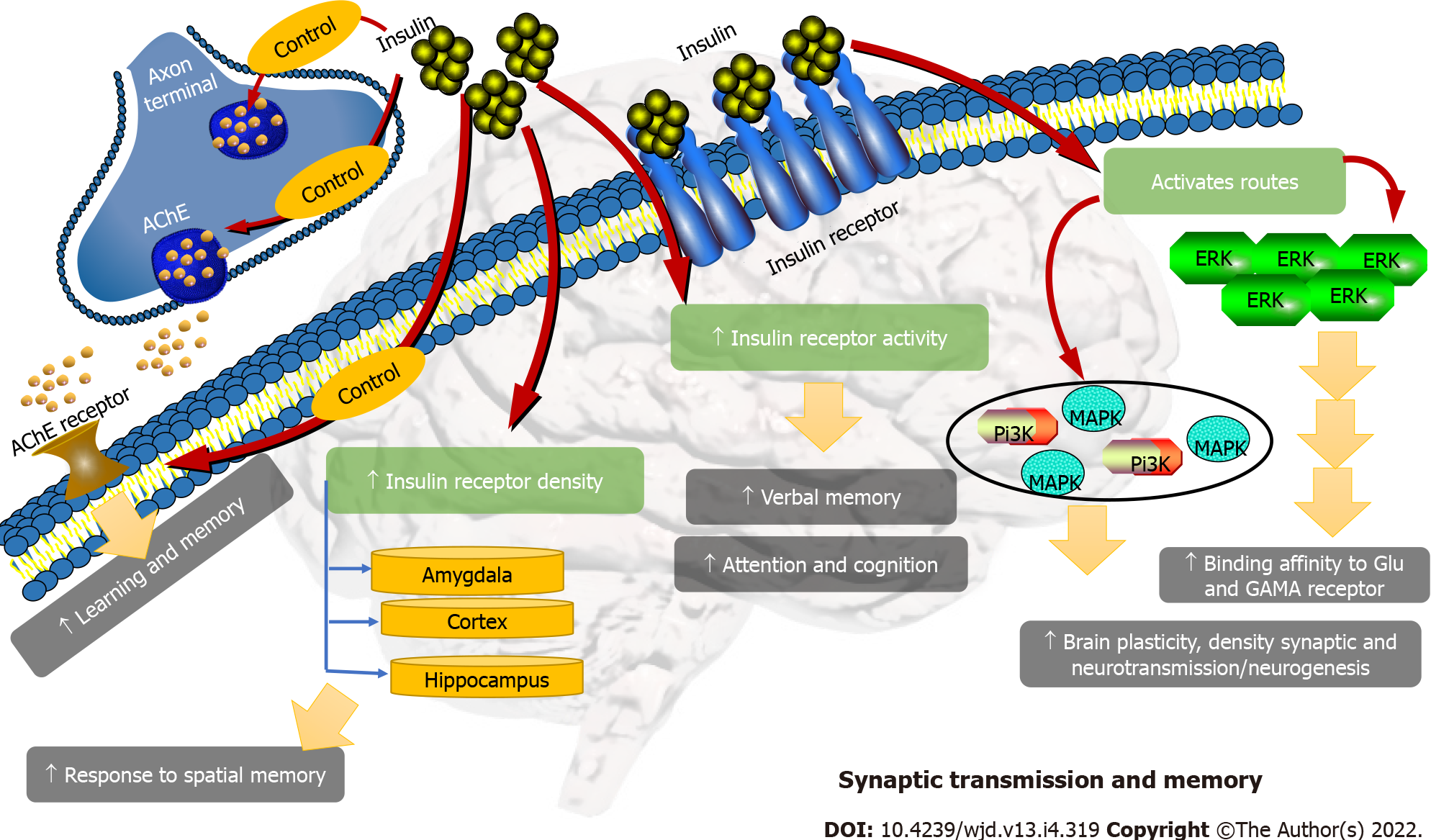
Figure 5 Synaptic transmission and memory.
Insulin increases the density of insulin receptors, its activity, the activation of routes such as phosphoinositide-3 kinase, mitogen-activated protein kinase, and extracellular signal-regulated kinase and regulates the binding of acetylcholine with its receptors, modulating cognition, memory, neurotransmission, and neurogenesis. Some pictures were taken from Qiagen Pathways. AChE: Acetylcholine; Pi3K: Phosphoinositide-3 kinase; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; ERK: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase.
- Citation: Ortiz GG, Huerta M, González-Usigli HA, Torres-Sánchez ED, Delgado-Lara DL, Pacheco-Moisés FP, Mireles-Ramírez MA, Torres-Mendoza BM, Moreno-Cih RI, Velázquez-Brizuela IE. Cognitive disorder and dementia in type 2 diabetes mellitus. World J Diabetes 2022; 13(4): 319-337
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v13/i4/319.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v13.i4.319