Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Diabetes. Oct 15, 2022; 13(10): 835-850
Published online Oct 15, 2022. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v13.i10.835
Published online Oct 15, 2022. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v13.i10.835
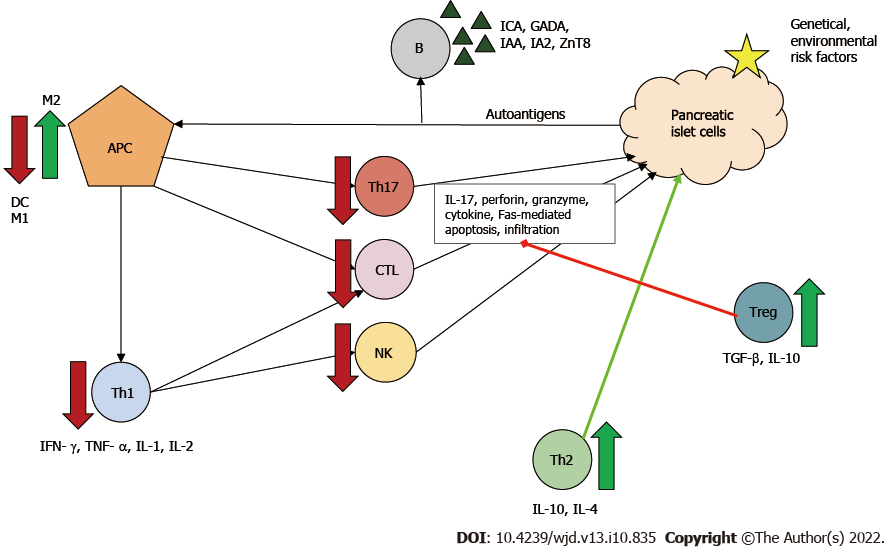
Figure 3 Immunoregulatory function of mesenchymal stem cells in type 1 diabetes mellitus.
The effects of mesenchymal stem cells ultimately result in downregulation in the proliferation and function of dendritic cells, cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs), helper T (Th) type 1 and type 17 cells, natural killer (NK) cells and type 1 macrophages (M1). Meanwhile, mesenchymal stem cells increase the number of type 2 macrophages (M2) and regulatory T cells (Tregs), which can inhibit effector T cells and stimulate Th type 2 protective cells. Red arrow/line: Downregulation/inhibition; Green arrow/line: Stimulation. APC: Antigen-presenting cell; B: B cell; DC: Dendritic cell; GADA: Glutamic-acid-decarboxylase antibody; IA2: Islet tyrosine phosphatase 2 antibody; IAA: Insulin autoantibody; ICA: Islet cell antibody; IL: Interleukin; IFN-γ: Interferon γ; TGF-β: Transforming growth factor β; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor α; ZnT8: Zinc transporter 8 antibody.
- Citation: Nagy G, Szekely TE, Somogyi A, Herold M, Herold Z. New therapeutic approaches for type 1 diabetes: Disease-modifying therapies. World J Diabetes 2022; 13(10): 835-850
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v13/i10/835.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v13.i10.835