Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Diabetes. Jan 15, 2022; 13(1): 37-53
Published online Jan 15, 2022. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v13.i1.37
Published online Jan 15, 2022. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v13.i1.37
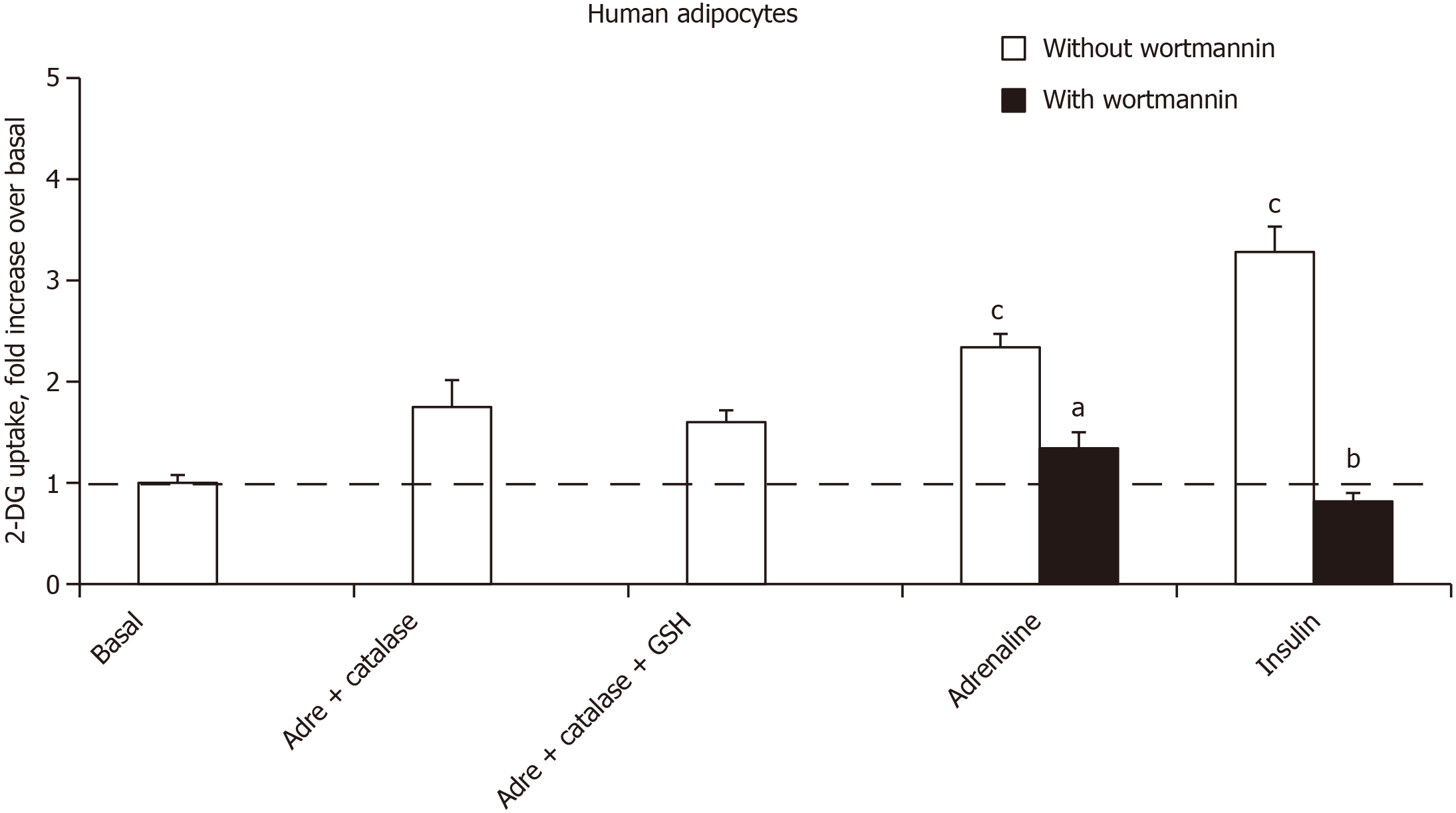
Figure 7 Inhibition of adrenaline-induced hexose uptake in human adipocytes by catalase, glutathione and wortmannin.
The pretreatment of adipocytes by catalase alone (5000 IU/mL) or in combination with 1 mmol/L glutathione was started 10 min before the addition of 1 mmol/L adrenaline, which was incubated for 45 min before performing 2-deoxyglucose uptake assay for 10 min. The mean ± standard error of the mean of 4 to 6 separate experiments is given as fold increase above basal 2-deoxyglucose uptake. A significant difference from basal was observed at: cP < 0.001; Different from 1 mmol/L adrenaline alone at: aP < 0.05, or from 100 nmol/L insulin alone at: bP < 0.001. 2-DG: 2-Deoxyglucose; adre: Adrenaline.
- Citation: Carpéné C, Boulet N, Grolleau JL, Morin N. High doses of catecholamines activate glucose transport in human adipocytes independently from adrenoceptor stimulation or vanadium addition. World J Diabetes 2022; 13(1): 37-53
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v13/i1/37.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v13.i1.37