Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Diabetes. Jan 15, 2022; 13(1): 37-53
Published online Jan 15, 2022. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v13.i1.37
Published online Jan 15, 2022. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v13.i1.37
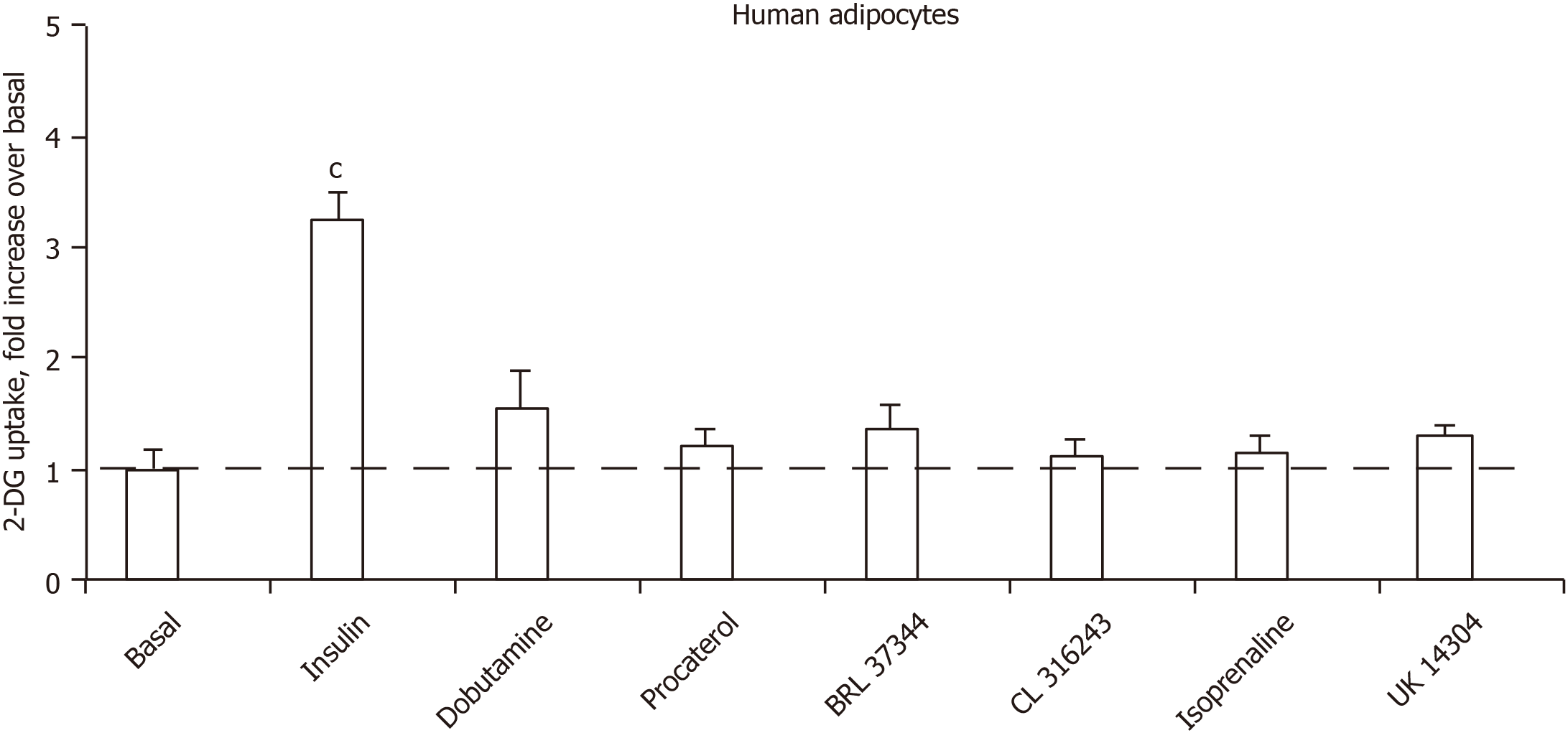
Figure 6 Influence of insulin, β- and α-adrenergic receptor agonists on hexose transport in human adipocytes.
2-Deoxyglucose uptake assay was performed without (basal) and with 100 nmol/L insulin or 1 µmol/L of the indicated adrenergic receptor agonists. Dobutamine: β1-AR agonist; procaterol: β2-AR agonist; BRL 37344 and CL 316243: β3-AR agonists; isoprenaline: pan-agonist of the three subtypes of β-ARs; UK 14304: α2-AR agonist. Glucose transport was expressed as fold increase relative to basal uptake set at 1.0 (dotted line). Each column is the mean ± standard error of the mean of 9-12 individual adipocyte preparations. Only insulin-induced uptake was significantly different from baseline at: cP < 0.001. 2-DG: 2-Deoxyglucose.
- Citation: Carpéné C, Boulet N, Grolleau JL, Morin N. High doses of catecholamines activate glucose transport in human adipocytes independently from adrenoceptor stimulation or vanadium addition. World J Diabetes 2022; 13(1): 37-53
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v13/i1/37.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v13.i1.37