Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Diabetes. Jan 15, 2022; 13(1): 37-53
Published online Jan 15, 2022. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v13.i1.37
Published online Jan 15, 2022. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v13.i1.37
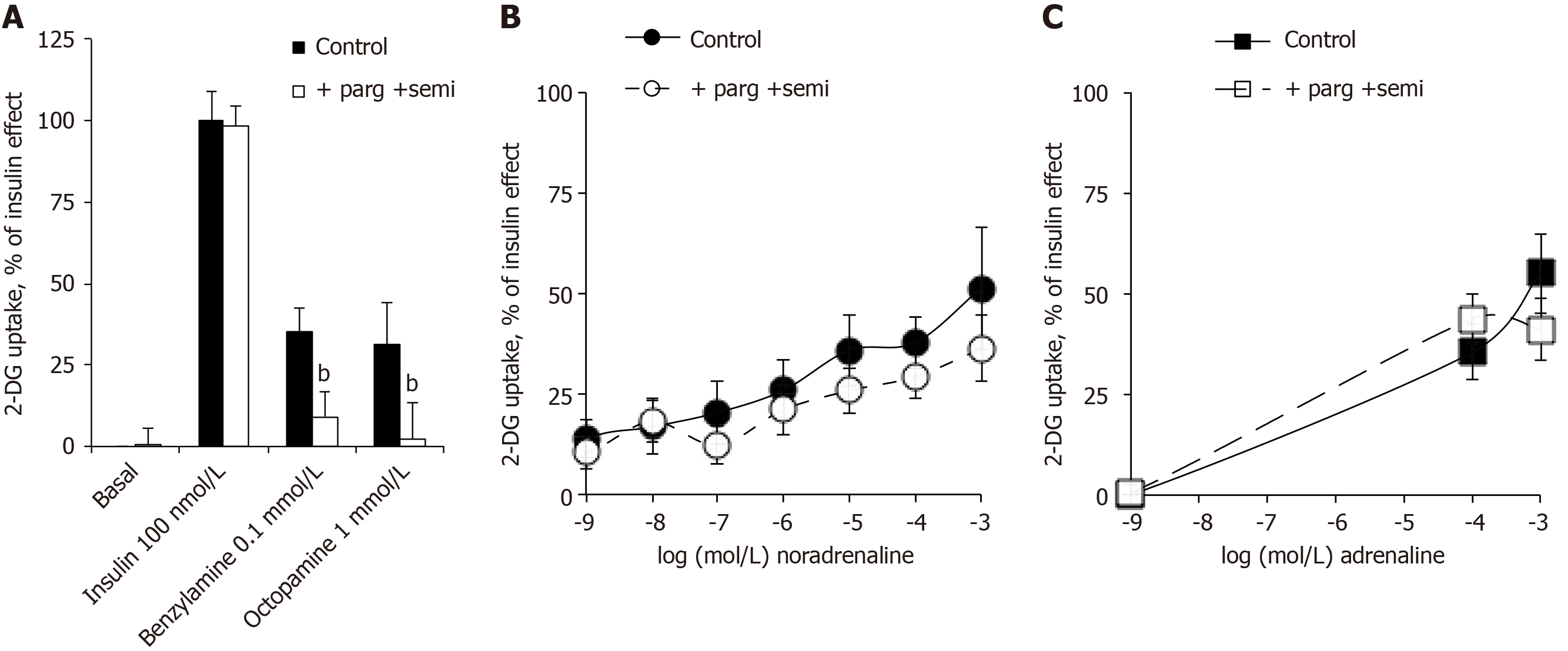
Figure 5 Inhibition by pargyline and semicarbazide of benzylamine and octopamine effects on hexose uptake in human adipocytes but not of noradrenaline and adrenaline effects.
Human fat cells were incubated in the presence of the indicated agents without (control, black symbols) and with the combination of 100 µmol/L pargyline plus 1 mmol/L semicarbazide (open symbols) before being subjected to 2-deoxyglucose uptake assay. A: Insulin, benzylamine and octopamine: mean ± standard error of the mean of 7 adipocyte preparations. A significant inhibition when compared to respective control was observed at: bP < 0.01. B: Increasing doses of noradrenaline: mean ± standard error of the mean of 13 cases. C: Indicated doses of adrenaline: mean ± standard error of the mean of 17 cases. No significant difference was found between inhibitor and respective control conditions. 2-DG: 2-Deoxyglucose; parg: Pargyline; semi: Semicarbazide.
- Citation: Carpéné C, Boulet N, Grolleau JL, Morin N. High doses of catecholamines activate glucose transport in human adipocytes independently from adrenoceptor stimulation or vanadium addition. World J Diabetes 2022; 13(1): 37-53
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v13/i1/37.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v13.i1.37