Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Diabetes. Jan 15, 2022; 13(1): 37-53
Published online Jan 15, 2022. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v13.i1.37
Published online Jan 15, 2022. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v13.i1.37
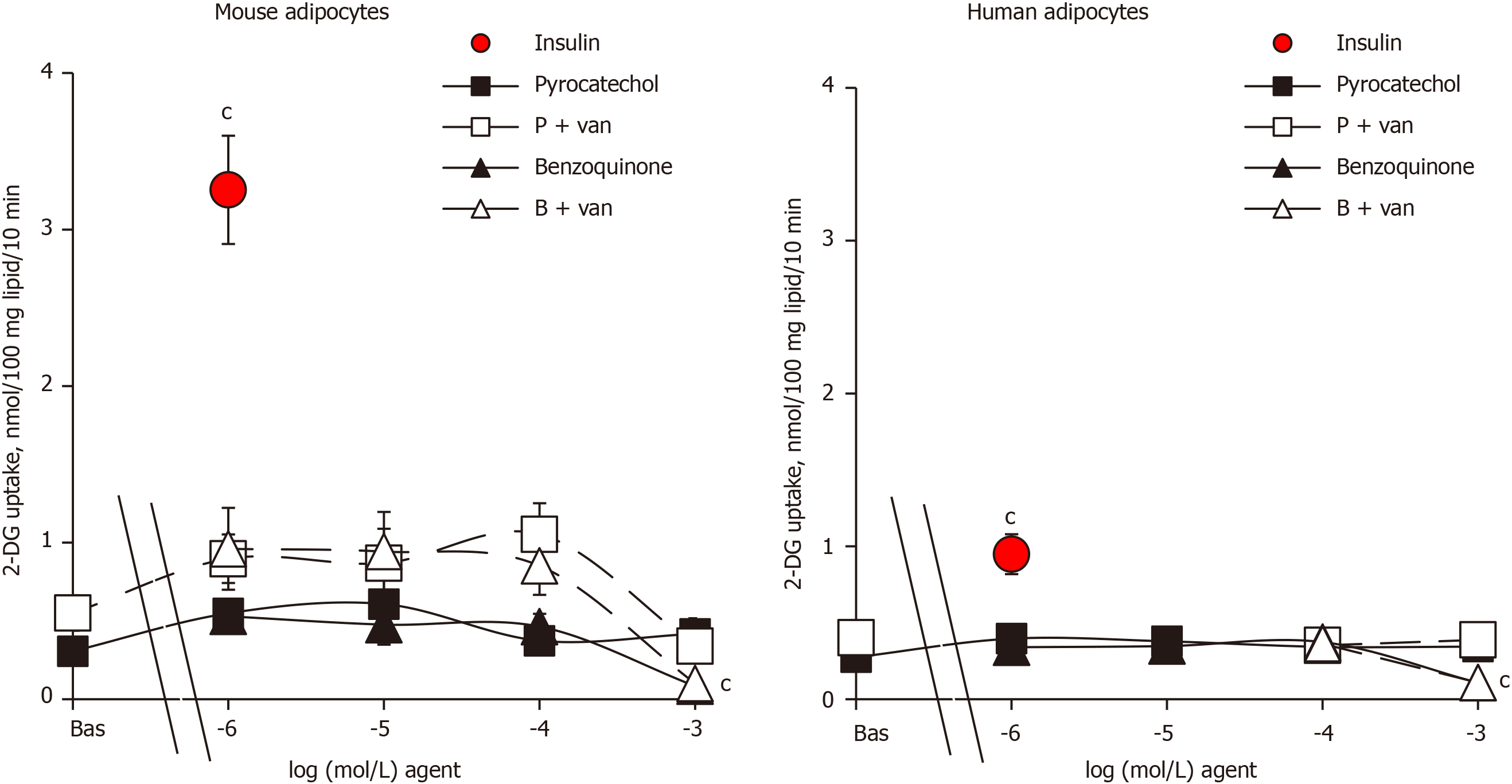
Figure 3 Lack of stimulatory influence of pyrocatechol and benzoquinone on hexose uptake in mouse and human adipocytes.
Mouse (left panel) and human (right panel) fat cells were incubated for 45 min with increasing concentrations (from 1 µmol/L to 1 mmol/L, indicated as log of molar concentration) of pyrocatechol (squares) or benzoquinone (triangles) without (closed symbols) or with 100 µmol/L vanadate (open symbols) just before assaying [3H]-2-deoxyglucose uptake for a 10-min period. Basal (without any agent added) and maximal hexose uptake in response to 1 µmol/L insulin (red circle, bovine hormone for mouse adipocytes and human recombinant protein for human adipocytes) are given with the same Y-axis scale for the sake of comparison. Mean ± standard error of the mean of 9 and 7 separate experiments for mouse and human adipocyte preparations containing 15 ± 2 and 20 ± 3 mg lipid/400 µL assay tube, respectively. Difference from basal uptake was significant at: cP < 0.001. 2-DG: 2-Deoxyglucose; B: Benzoquinone; van: Vanadate; P: Pyrocatechol; Bas: Basal.
- Citation: Carpéné C, Boulet N, Grolleau JL, Morin N. High doses of catecholamines activate glucose transport in human adipocytes independently from adrenoceptor stimulation or vanadium addition. World J Diabetes 2022; 13(1): 37-53
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v13/i1/37.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v13.i1.37