Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Diabetes. Jul 15, 2021; 12(7): 1102-1115
Published online Jul 15, 2021. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v12.i7.1102
Published online Jul 15, 2021. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v12.i7.1102
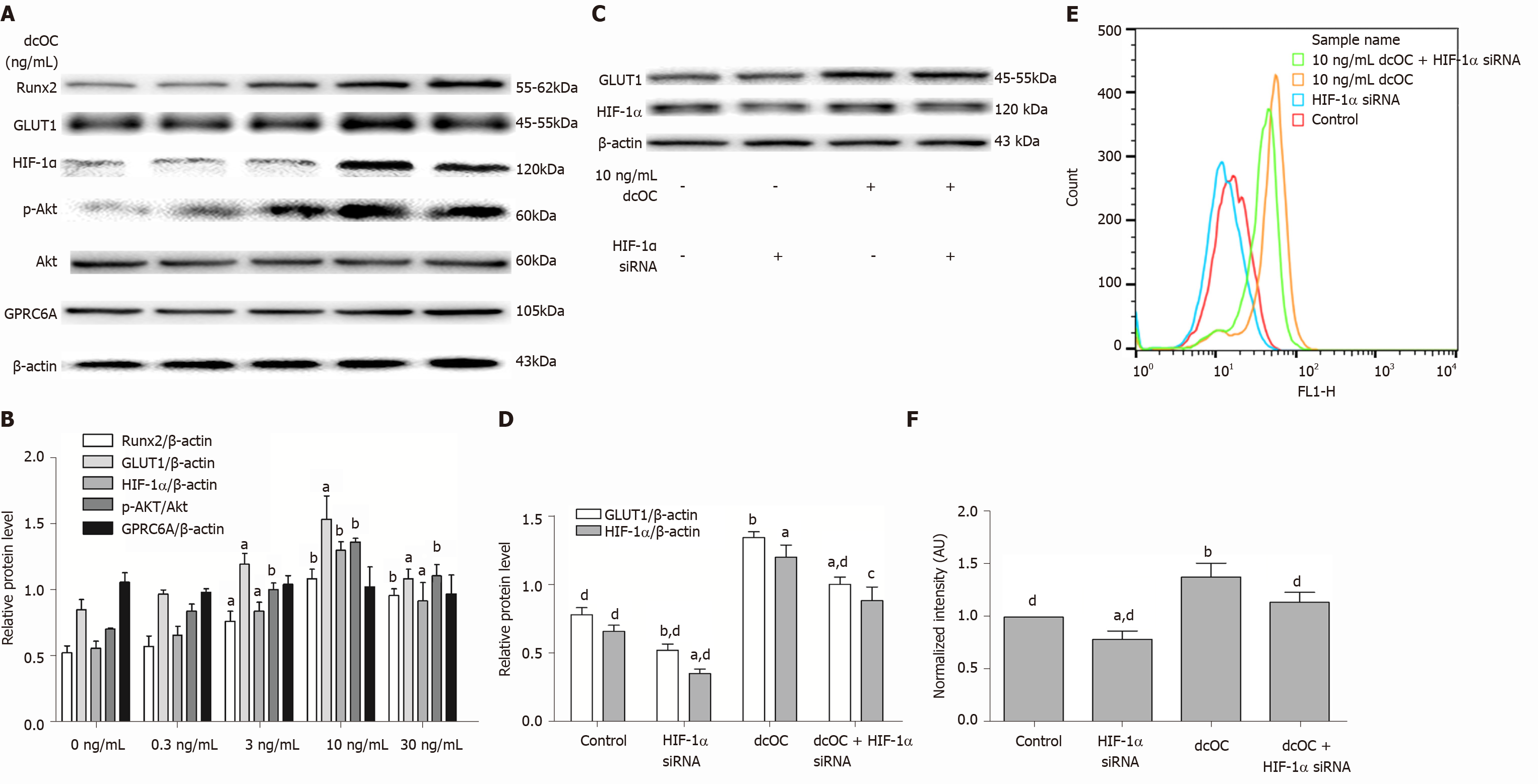
Figure 4 Promotional effect of decarboxylated osteocalcin on glucose uptake after long-term stimulation (72 h) in MG63 cells.
A: Protein bands; B: Relative protein levels of GPRC6A (G protein-coupled receptor family C group 6 subtype A), p-Akt (Ser473)/Akt, hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha (HIF-1α), glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1), and Runx2 after decarboxylated osteocalcin (dcOC) stimulation for 72 h at different concentrations; C: Protein bands; D: Relative protein levels of HIF-1α and GLUT1; E: The distribution of fluorescence intensities which represented 2-Deoxy-2-[(7-nitro-2,1,3-benzoxadiazol-4-yl)amino]-D-glucose (2-NBDG) uptake; F: The normalized fluorescence intensity corresponding to 2-NBDG uptake. The MG63 cells in C-F were treated with dcOC (10 ng/mL) 72 h and (or) were transfected with HIF-1α siRNA. The data are representative of three independent experiments performed in triplicate. B: aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs untreated cells; D and F: aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs the control group; cP < 0.05, dP < 0.01 vs the dcOC-only group. dcOC: Decarboxylated osteocalcin; HIF-1α: Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha; GLUT1: Glucose transporter 1; GPRC6A: G protein-coupled receptor family C group 6 subtype A.
- Citation: Jin S, Chang XC, Wen J, Yang J, Ao N, Zhang KY, Suo LN, Du J. Decarboxylated osteocalcin, a possible drug for type 2 diabetes, triggers glucose uptake in MG63 cells. World J Diabetes 2021; 12(7): 1102-1115
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v12/i7/1102.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v12.i7.1102