Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Diabetes. Jun 15, 2021; 12(6): 794-809
Published online Jun 15, 2021. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v12.i6.794
Published online Jun 15, 2021. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v12.i6.794
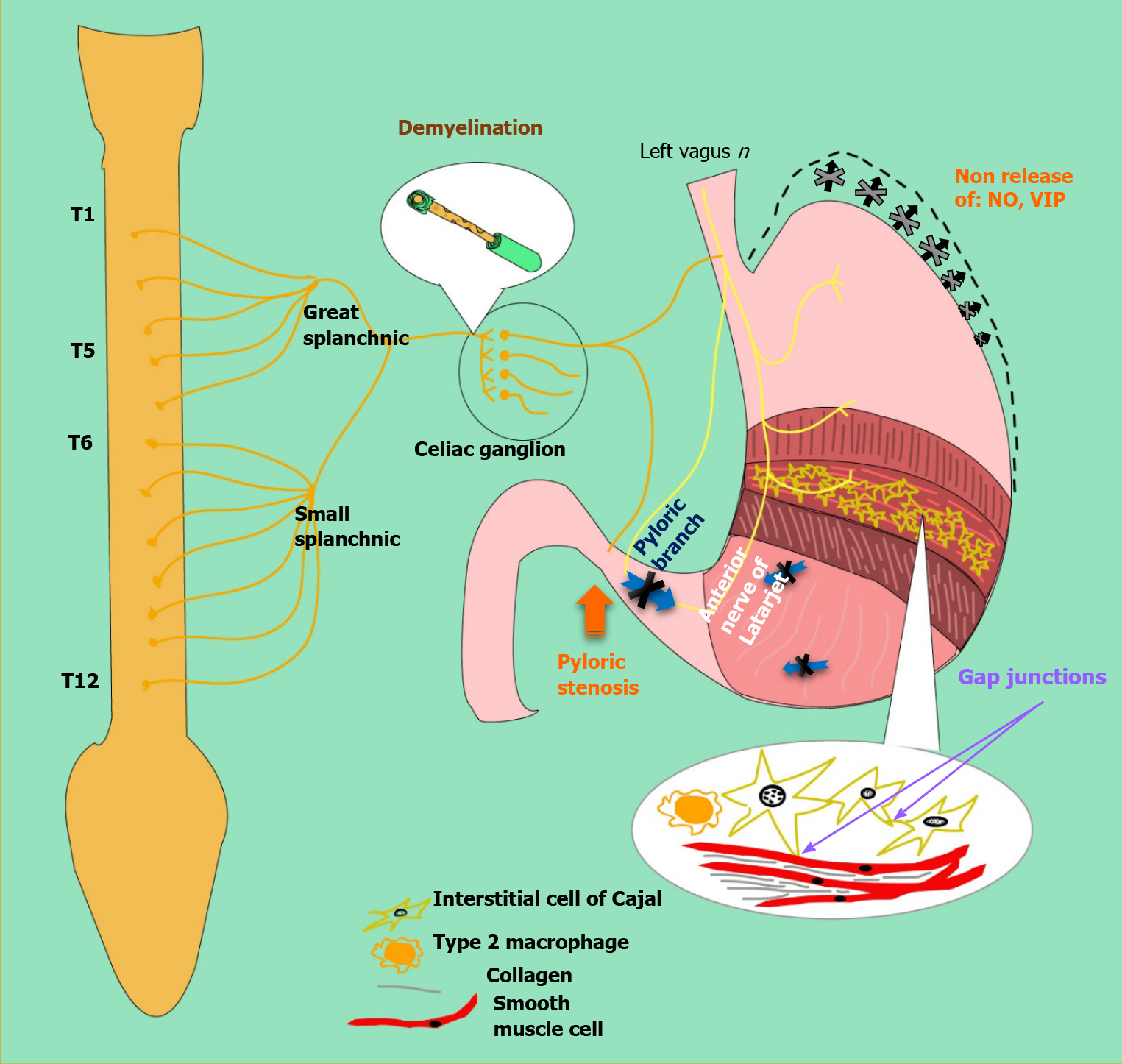
Figure 3 Pathophysiology of diabetic gastroparesis.
Dysfunction in the Sympathetic nervous system (Celiac Ganglion), parasympathetic nervous system (Vagus Nerve) and enteric nervous system (Myenteric Interstitial cells of Cajal). Results in the dysfunction of emptying mechanism of the antral pump: phase of propulsion, emptying, and retropulsion (blue arrows), decrease of relaxes to accommodate meal (black arrows), loss of Nitric Oxide synthase in the enteric nerves (fundus, pylori), loss of ICC, Type 2 Macrophage altered function with loss of cytoprotective to ICC, smooth muscle atrophy, and increased smooth muscle fibrosis. NO: Nitric oxide; VIP: Vasoactive inhibitory peptide; ICC: Interstitial of cajal cell.
- Citation: Concepción Zavaleta MJ, Gonzáles Yovera JG, Moreno Marreros DM, Rafael Robles LDP, Palomino Taype KR, Soto Gálvez KN, Arriola Torres LF, Coronado Arroyo JC, Concepción Urteaga LA. Diabetic gastroenteropathy: An underdiagnosed complication . World J Diabetes 2021; 12(6): 794-809
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v12/i6/794.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v12.i6.794