Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Diabetes. May 15, 2021; 12(5): 658-672
Published online May 15, 2021. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v12.i5.658
Published online May 15, 2021. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v12.i5.658
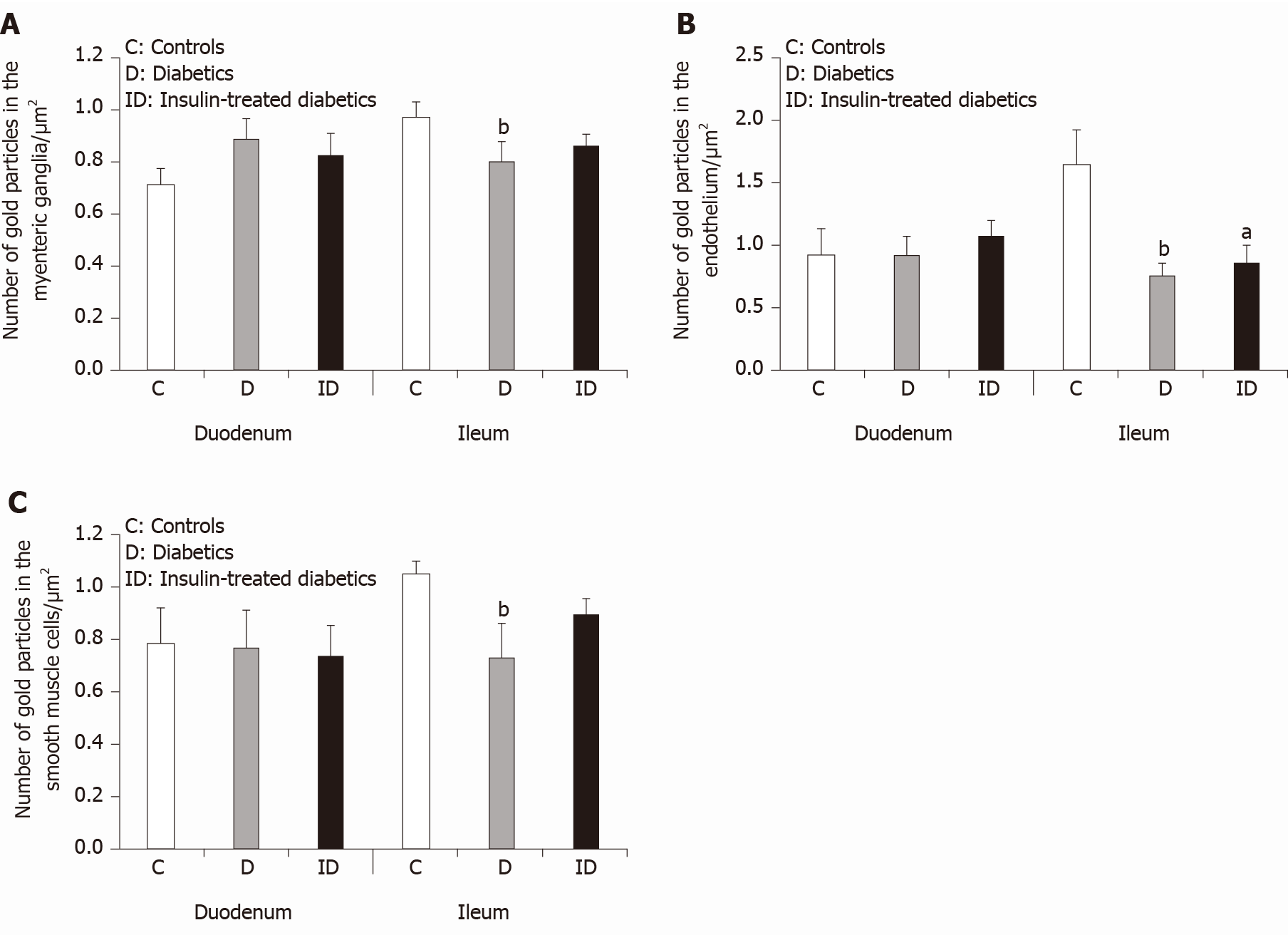
Figure 5 Quantitative changes in matrix metalloproteinase 9 expression in different cellular compartments.
A: Quantitative evaluation of matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP9)-labeling gold particles in myenteric ganglia; B: Capillary endothelium; and C: Intestinal smooth muscle cells from different gut segments of control, diabetic, and insulin-treated diabetic rats. In diabetics, the number of MMP9-labeling gold particles was significantly decreased in all cellular compartments of the ileum, while it was unchanged in the duodenum relative to controls. The number of gold particles was closer to the control values after immediate insulin treatment. Data are expressed as means ± SEM. aP < 0.05 and bP < 0.01 (relative to controls).
- Citation: Bódi N, Mezei D, Chakraborty P, Szalai Z, Barta BP, Balázs J, Rázga Z, Hermesz E, Bagyánszki M. Diabetes-related intestinal region-specific thickening of ganglionic basement membrane and regionally decreased matrix metalloproteinase 9 expression in myenteric ganglia. World J Diabetes 2021; 12(5): 658-672
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v12/i5/658.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v12.i5.658