Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Diabetes. May 15, 2021; 12(5): 524-540
Published online May 15, 2021. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v12.i5.524
Published online May 15, 2021. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v12.i5.524
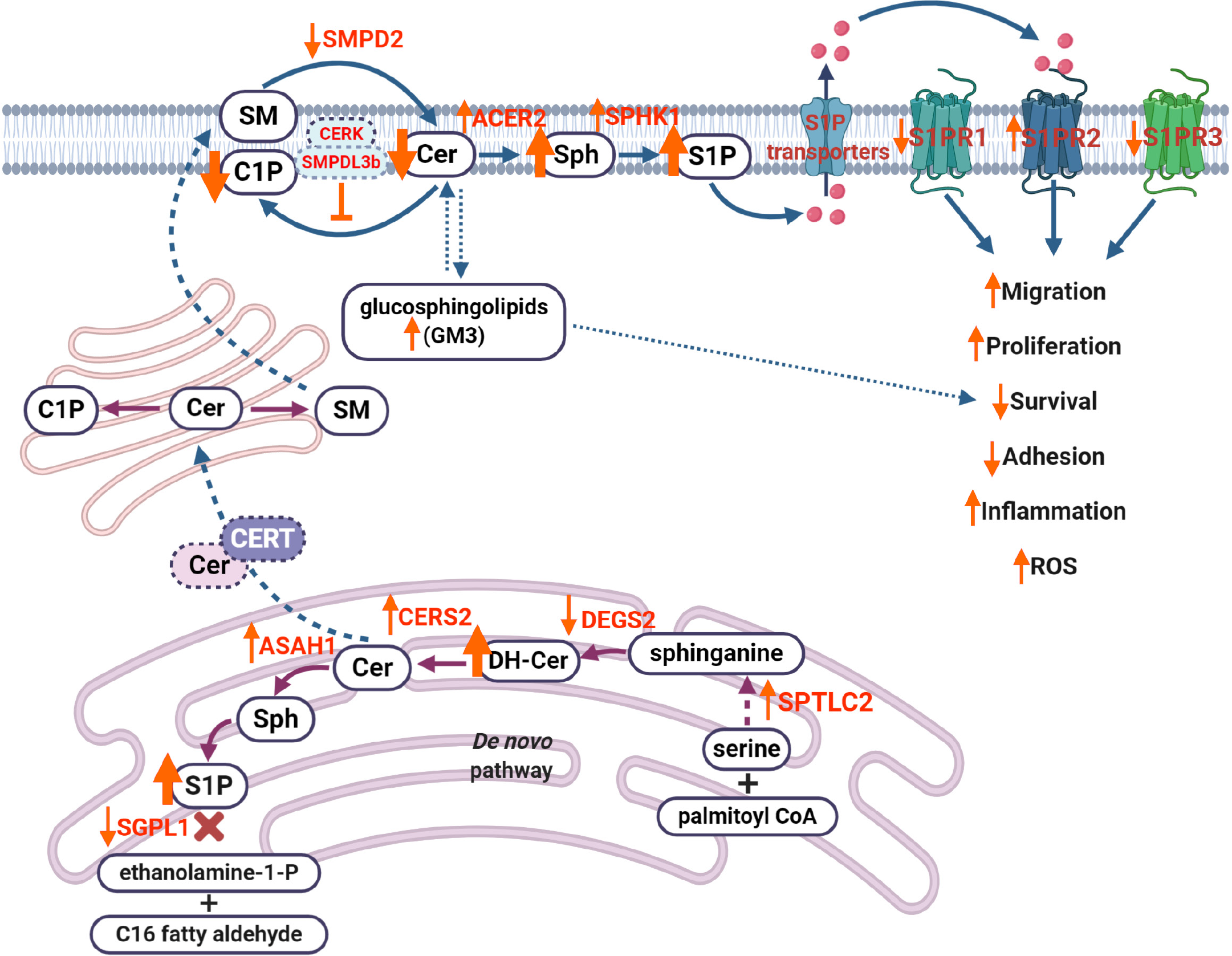
Figure 3 Dysregulation of sphingolipid metabolism contributes to the progression of diabetic kidney disease.
Decreased activity of desaturase (DEGS2) results in the accumulation of dihydroceramides. Increased activity of ceramide synthase 2 (CERS2) leads to increased production of ceramide (Cer), which leads to increased production of sphingosine (Sph) and sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) via decreased activity of sphingosine-1-phosphate lyase 1. Cer can also be translocated to the Golgi apparatus via ceramide transport protein, where it results in production of sphingomyelin. At the plasma membrane, decreased activity of sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase 2 affects Cer production, while elevated activity of alkaline ceramidase 2 increases levels of Sph, which, in turn, leads to accumulation of S1P via increased activity of sphingosine kinase 1. Overproduction of S1P results in increased S1P efflux via S1P transporters (such as ATP-binding cassette transporters ABCA1, ABCG1, ABCC1 and S1P transporter SPNS2), where S1P can act as a paracrine factor to activate S1P receptor signaling (primarily, S1P receptors 1-3, S1PR1, S1PR2, S1PR3), leading to dysregulation of many cellular processes, including migration, proliferation, survival or inflammation. Accumulation of gangliosides (GM3) can also affect cell survival in diabetic kidney disease. This image was created using BioRender software (www.BioRender.com). SMPD2: Sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase 2; SM: Sphingomyelin; C1P: Ceramide-1-phosphate; CERK: Ceramide kinase; SMPDL3b: Sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase acid-like 3b; Cer: Ceramide; Sph: Sphingosine; S1P: Sphingosine-1-phosphate; S1PR1: Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1; S1PR2: Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 2; S1PR3: Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 3; GM3: Ganglioside M3; CERT: Ceramide transport protein; SGPL1: Sphingosine-1-phosphate lyase 1; DH-Cer: Dihydroceramide; ASAH1: N-acylsphingosine amidohydrolase 1; CERS2: Ceramide synthase 2; DEGS2: Delta(4)-desaturase, sphingolipid 2; SPTLC2: Serine palmitoyltransferase 2; CoA: Acyl-coenzyme A; ROS: Reactive oxygen species.
- Citation: Mitrofanova A, Burke G, Merscher S, Fornoni A. New insights into renal lipid dysmetabolism in diabetic kidney disease. World J Diabetes 2021; 12(5): 524-540
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v12/i5/524.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v12.i5.524