Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Diabetes. May 15, 2021; 12(5): 524-540
Published online May 15, 2021. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v12.i5.524
Published online May 15, 2021. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v12.i5.524
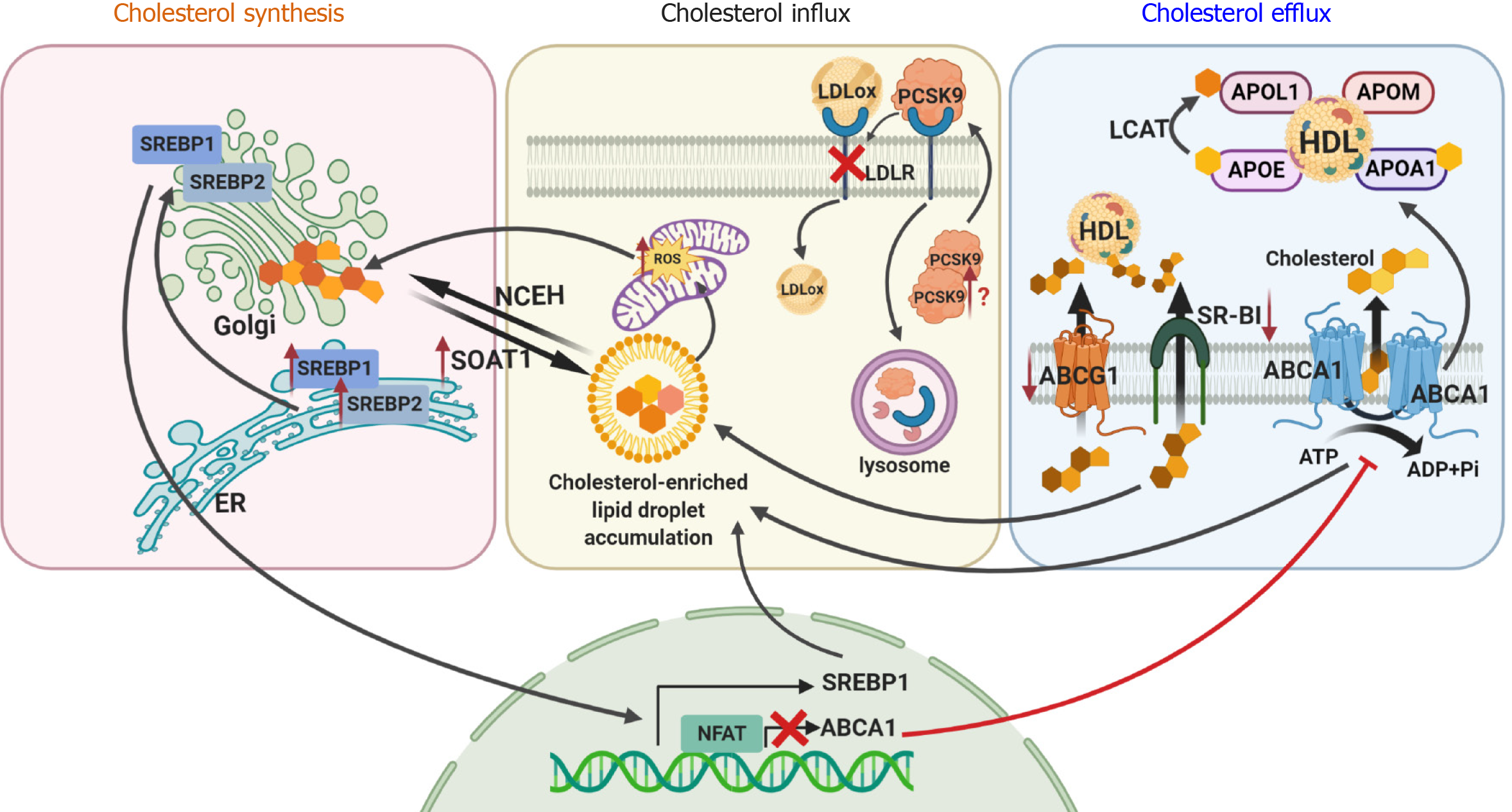
Figure 1 Cellular dyslipidemia in diabetic kidney disease affects cholesterol synthesis, influx and efflux.
Sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 or 2 (SREBP1 and SREBP2) is transported from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi apparatus, where it is cleaved followed by translocation to the nucleus to initiate cholesterol synthesis. Newly synthesized free cholesterol is then converted into esterified cholesterol by sterol O-acyltransferase 1 (SOAT1) or is transported to the plasma membrane for efflux by ATP-binding cassette subfamily A member 1 (ABCA1), subfamily G member 1 (ABCG1) or scavenger receptor class B type I (SR-BI). Cholesterol uptake from circulating low density lipoproteins (LDLs) is mediated by LDL receptor (LDLR). In diabetic kidney disease (DKD), overexpression of SREBP1 and SREBP2 and decreased expression of ABCA1, ABCG1 and SR-BI results in accumulation of cholesterol inside a cell and increased reactive oxygen species production. Accumulation of free cholesterol activates SOAT1, leading to over-production of esterified cholesterol, which is toxic to cells. Overexpression of proprotein convertase subtilisin kexin 9 may also contribute to DKD via enhanced degradation of the LDLR, resulting in increased levels of circulating LDL cholesterol. This image was created using BioRender software (www.BioRender.com). SREBP1: Sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1; SREBP2: Sterol regulatory element-binding protein 2; ER: Endoplasmic reticulum; SOAT1: Sterol O-acyltransferase 1; NCEH: Neutral cholesterol ester hydrolase; LDLox: Oxidized low density lipoprotein; PCSK9: Proprotein convertase subtilisin kexin 9; LDLR: Low density lipoprotein receptor; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; LCAT: Lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase; APOL1: Apolipoprotein L1; APOE: Apolipoprotein E; APOM: Apolipoprotein M; APOA1: Apolipoprotein A1; HDL: High density lipoprotein; ABCA1: ATP-binding cassette subfamily A member 1; ABCG1: Subfamily G member 1; SR-BI: Scavenger receptor class B type I; ATP: Adenosine triphosphate; ADP: Adenosine diphosphate; Pi: Inorganic phosphorus.
- Citation: Mitrofanova A, Burke G, Merscher S, Fornoni A. New insights into renal lipid dysmetabolism in diabetic kidney disease. World J Diabetes 2021; 12(5): 524-540
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v12/i5/524.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v12.i5.524