Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Diabetes. Apr 15, 2021; 12(4): 383-406
Published online Apr 15, 2021. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v12.i4.383
Published online Apr 15, 2021. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v12.i4.383
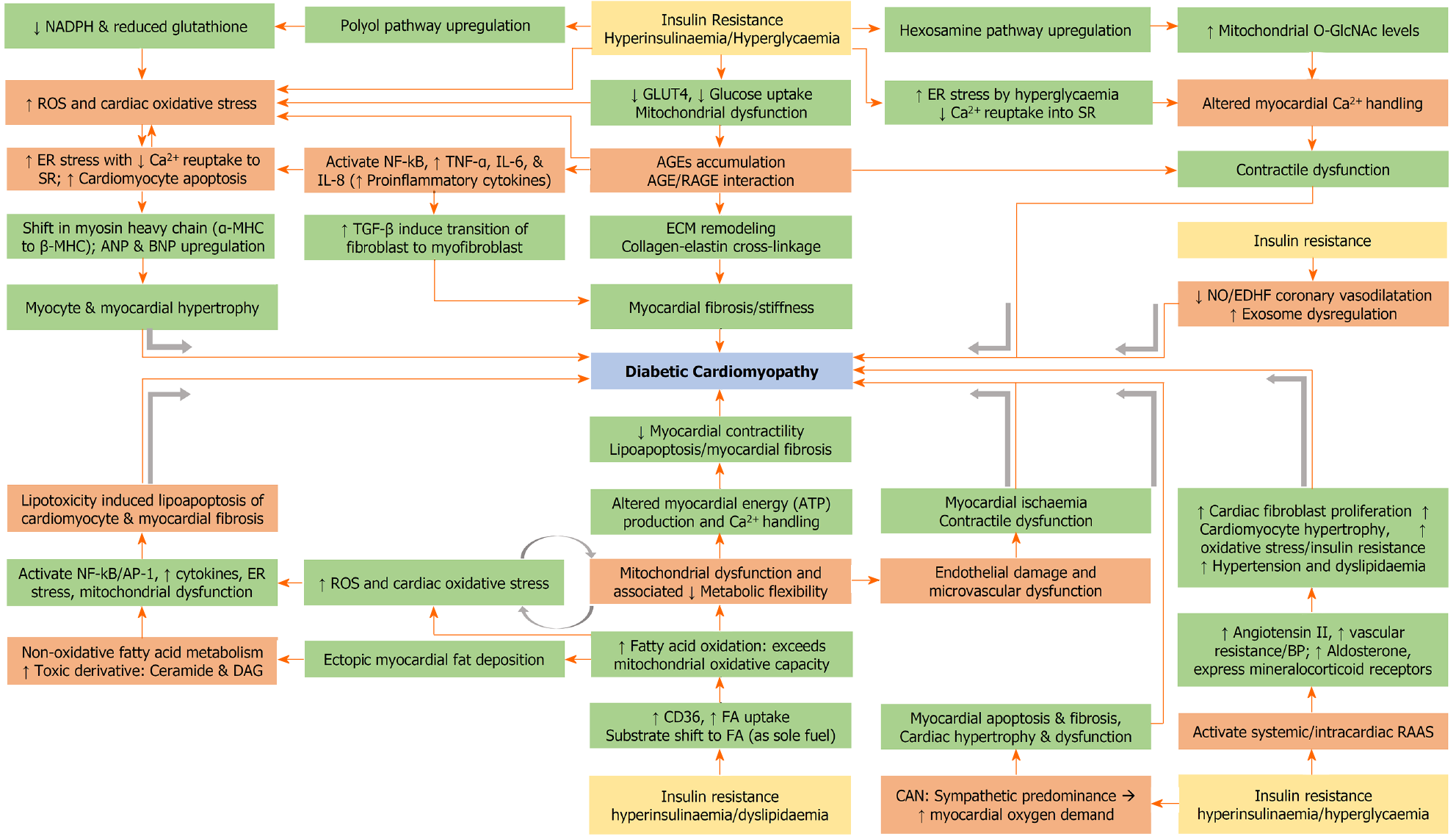
Figure 3 Pathophysiology of diabetic cardiomyopathy.
NADPH: Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; GLUT: Glucose transporter; ER: Endoplasmic reticulum; SR: Sarcoplasmic reticulum; NF-kB: Nuclear factor-kB; TNF-α: Tumour necrosis factor-α; IL-6: Interleukin-6; IL-8: Interleukin-8; AGE: Advanced glycation end products; RAGE: Receptors for AGE; MHC: Myosin heavy chain; ANP: Atrial natriuretic peptide; BNP: Brain natriuretic peptide; TGF-β: Transforming growth factor-β; ECM: Extracellular matrix; NO: Nitric oxide; EDHF: Endothelium-derived hyperpolarising factor; ATP: Adenosine triphosphate; AP-1: Activator protein-1; BP: Blood pressure; DAG: Diacyl glycerol; FA: Fatty acid; CAN: Cardiac autonomic neuropathy; RAAS: Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system.
- Citation: Rajbhandari J, Fernandez CJ, Agarwal M, Yeap BXY, Pappachan JM. Diabetic heart disease: A clinical update. World J Diabetes 2021; 12(4): 383-406
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v12/i4/383.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v12.i4.383