Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Diabetes. Nov 15, 2021; 12(11): 1875-1893
Published online Nov 15, 2021. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v12.i11.1875
Published online Nov 15, 2021. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v12.i11.1875
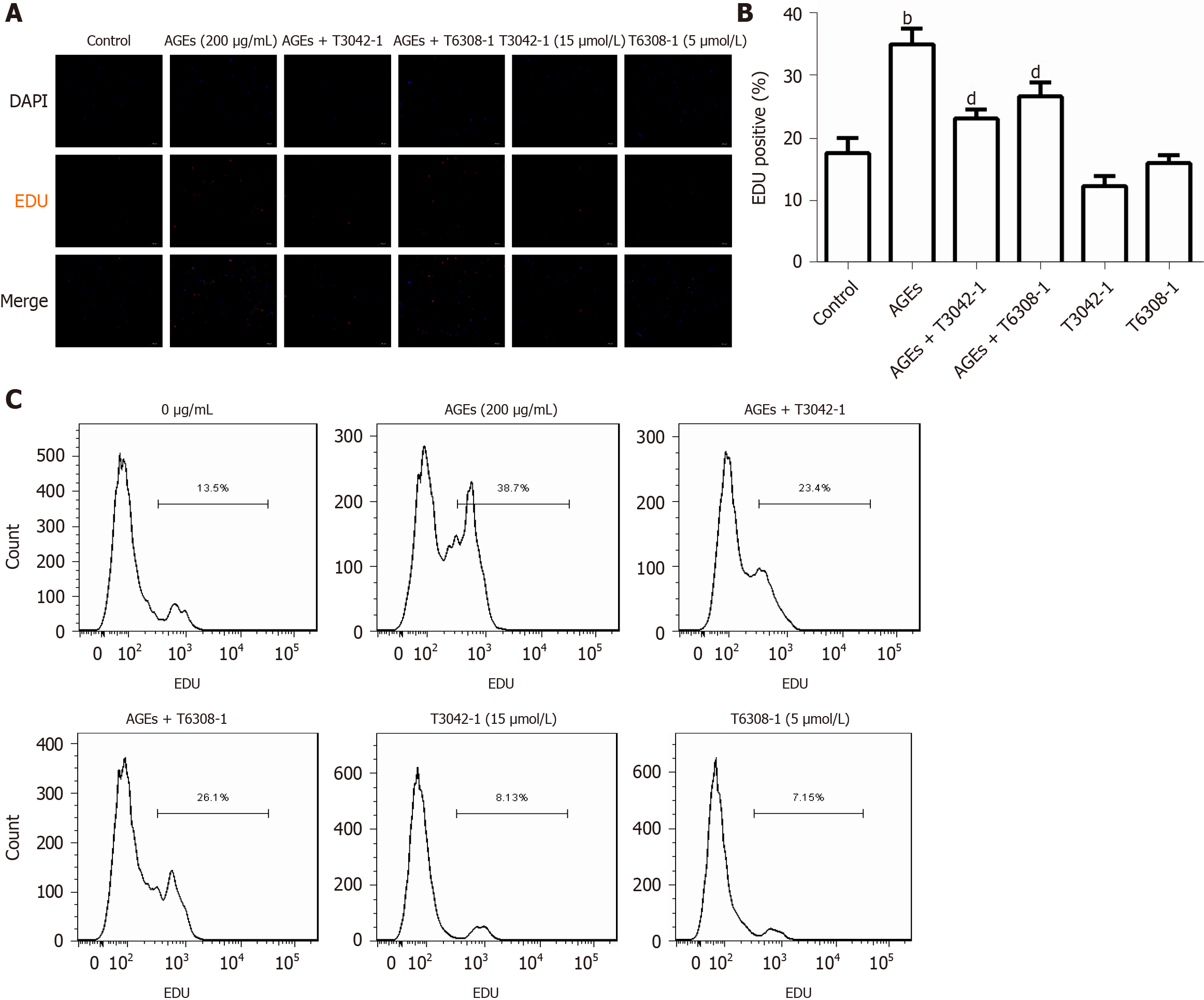
Figure 7 Effects of the Janus kinase 2 inhibitor and signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 inhibitor on advanced glycation end products-induced rat aortic vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation (n = 6).
Cells were treated with 200 µg/mL advanced glycation end products (AGEs) and/or 15 μmol/L Janus kinase 2 inhibitor (T3042-1) and/or 5 μmol/L signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 inhibitor (T6308-1). A: Fluorescence microscopy image of 5-ethynyl-2-deoxyuridine (EdU) staining; B: Percentage of EDU-positive cells in A. bP < 0.01 compared with the control group, dP < 0.01 compared with the advanced glycation end products group; C: Flow cytometry analysis of EdU staining. Data were obtained from six independent experiments. AGEs: Advanced glycation end products; EDU: 5-ethynyl-2-deoxyuridine.
- Citation: Xiao ZL, Ma LP, Yang DF, Yang M, Li ZY, Chen MF. Profilin-1 is involved in macroangiopathy induced by advanced glycation end products via vascular remodeling and inflammation. World J Diabetes 2021; 12(11): 1875-1893
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v12/i11/1875.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v12.i11.1875