Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Diabetes. Oct 15, 2021; 12(10): 1750-1764
Published online Oct 15, 2021. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v12.i10.1750
Published online Oct 15, 2021. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v12.i10.1750
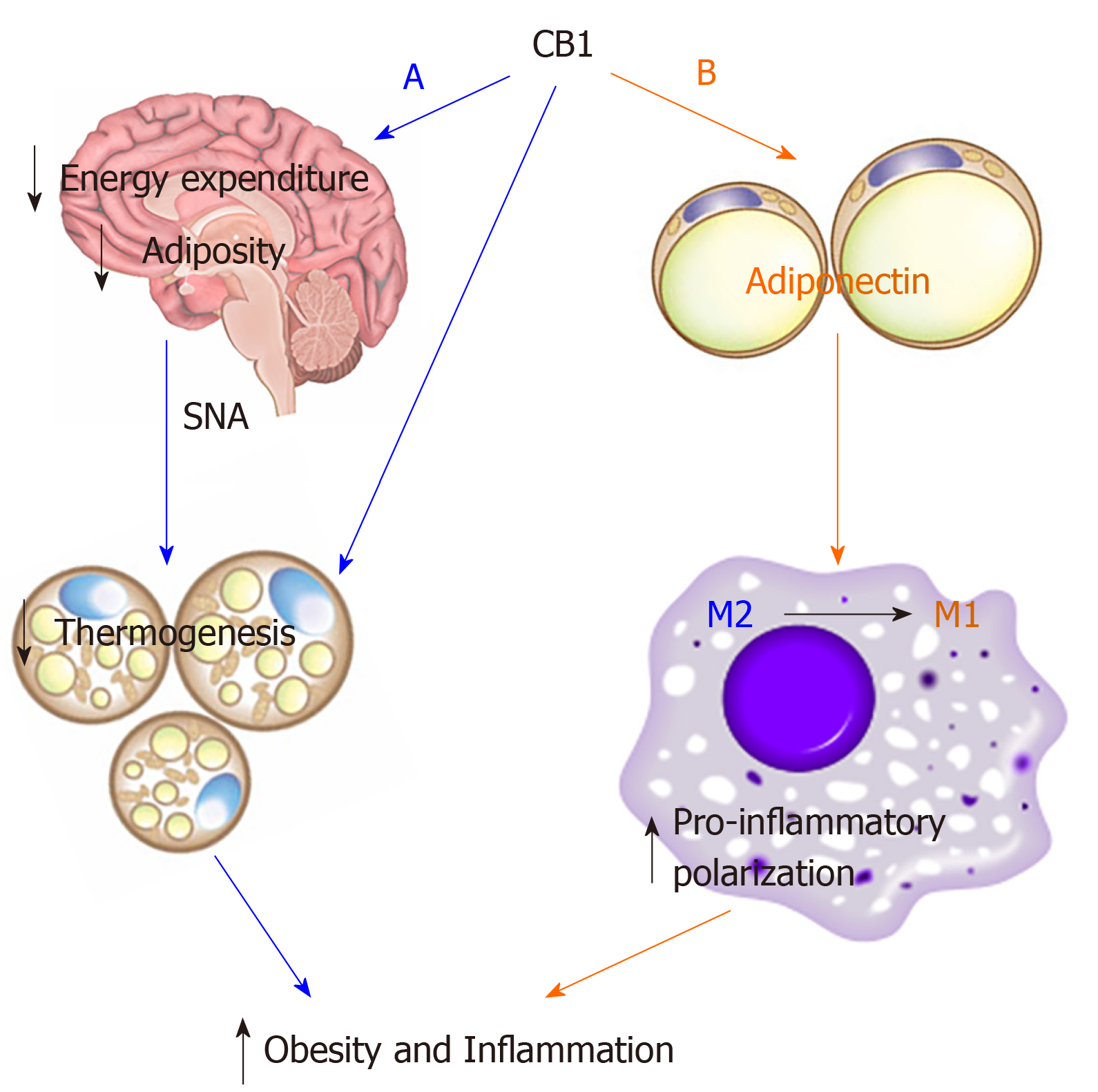
Figure 6 Schematic diagram of summary.
Cannabinoid type 1 receptor (CB1) utilizes differential mechanisms in control of metabolism and inflammation. A: CB1 decreases thermogenesis in BAT through sympathetic nerve activity to reduce energy expenditure and adiposity. So the effect of CB1 on metabolism is adiponectin-independent; B: CB1 suppresses adiponectin in adipose tissue, which diminishes the anti-inflammatory effect of adiponectin, thus promoting macrophage pro-inflammatory polarization. So the effect of CB1 on inflammation is adiponectin-dependent. Thus, CB1 utilizes differential mechanisms in control of metabolism and inflammation: its effect on metabolism is adiponectin-independent while effects on inflammation are adiponectin-dependent. Thus, adiponectin is not required for CB1-mediated metabolism, but is required for CB1-mediated inflammation.
- Citation: Wei Q, Lee JH, Wu CS, Zang QS, Guo S, Lu HC, Sun Y. Metabolic and inflammatory functions of cannabinoid receptor type 1 are differentially modulated by adiponectin. World J Diabetes 2021; 12(10): 1750-1764
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v12/i10/1750.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v12.i10.1750