Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Diabetes. Sep 15, 2020; 11(9): 374-390
Published online Sep 15, 2020. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v11.i9.374
Published online Sep 15, 2020. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v11.i9.374
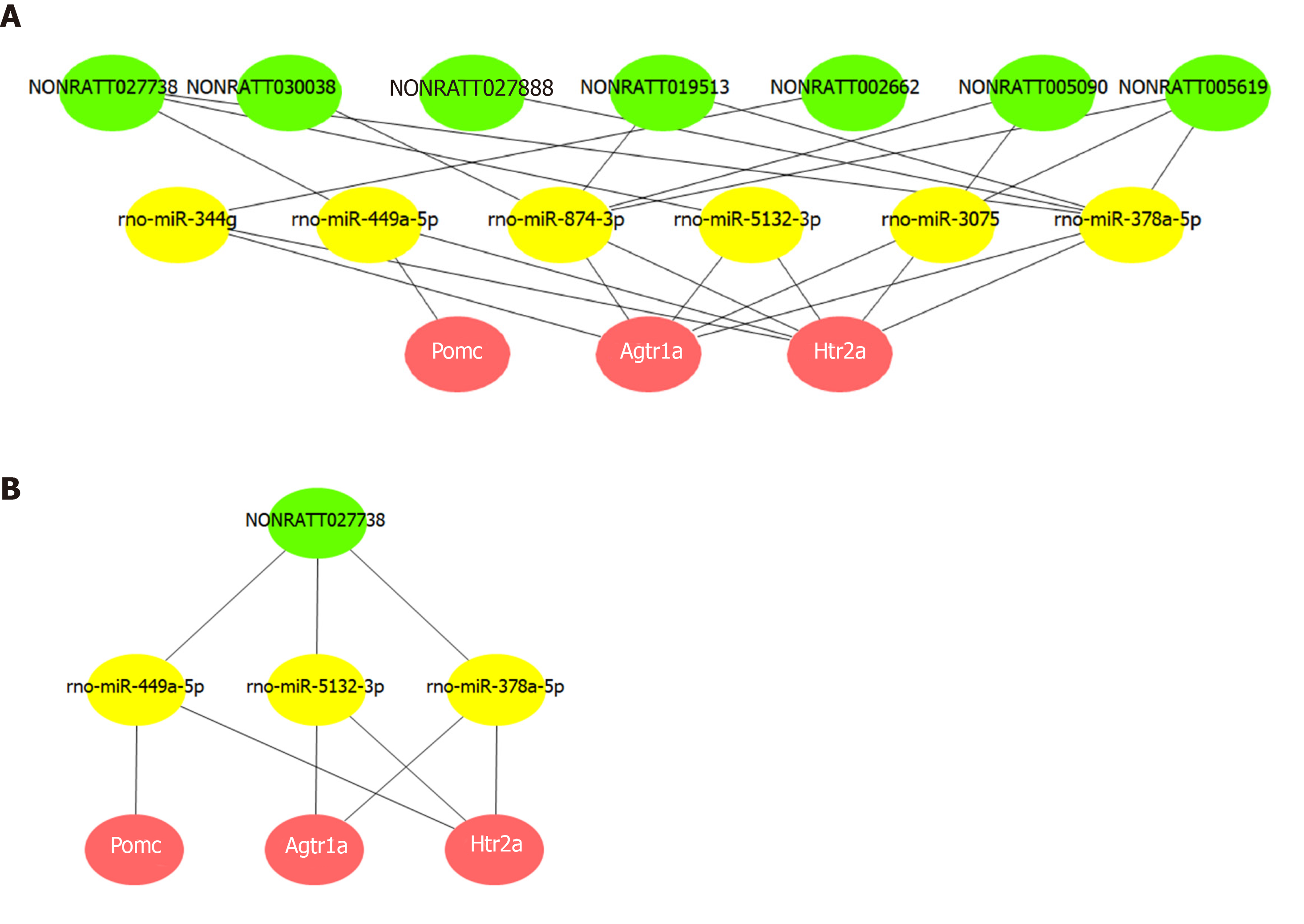
Figure 6 Competing endogenous RNA network of key long noncoding RNAs and Pomc, Htr2a, and Agtr1a.
A: The competing endogenous RNA network was constructed via common miRNAs that could bind to these 11 long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs), as well as the three hub mRNAs. Based on the intersection of the predictions from miRanda and TargetScan, seven lncRNAs were found to competitively bind six miRNAs, thereby affecting the expression and function of the hub mRNAs. B: Further network analysis indicated that NONRATT027738 can regulate all the three hub mRNAs (Pomc, Htr2a, and Agtr1a) through miRNAs (rno-miR-449a-5p, rno-miR-5132-3p, and rno-miR-378a-5p).
- Citation: Cui LJ, Bai T, Zhi LP, Liu ZH, Liu T, Xue H, Yang HH, Yang XH, Zhang M, Niu YR, Liu YF, Zhang Y. Analysis of long noncoding RNA-associated competing endogenous RNA network in glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist-mediated protection in β cells. World J Diabetes 2020; 11(9): 374-390
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v11/i9/374.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v11.i9.374