Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Diabetes. May 15, 2020; 11(5): 182-192
Published online May 15, 2020. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v11.i5.182
Published online May 15, 2020. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v11.i5.182
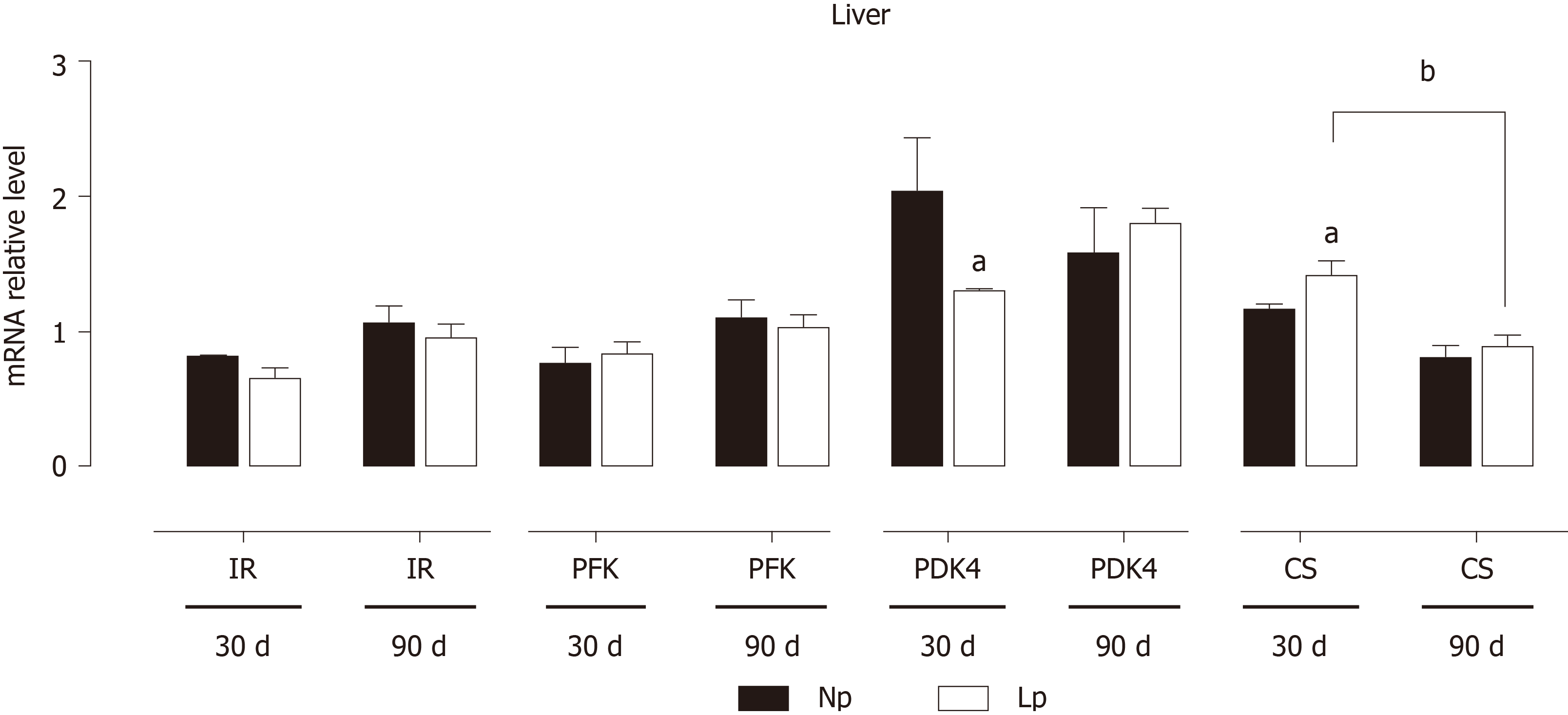
Figure 5 Expression of insulin receptor, glycolytic genes and Krebs cycle genes in the liver of rats.
Rats were exposed to maternal low protein diet during gestation and lactation, and gene expression of insulin receptor, phosphofructokinase, pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4 and citrate synthase was analyzed by quantitative reverse transcription PCR. Data are shown as mean ± standard error means and analyzed by two-way ANOVA with the mother’s diet (normal protein; low protein) and age (30 d, 90 d) as variable factors. Bonferroni’s post hoc test was used. Differences between diet groups are indicated by asterisks; differences between ages are indicated by bars. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01. NP: Normal protein; LP: Low protein; CS: Citrate synthase; PDK4: Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4; PFK: Phosphofructokinase; IR: Insulin receptor.
- Citation: de Oliveira Lira A, de Brito Alves JL, Pinheiro Fernandes M, Vasconcelos D, Santana DF, da Costa-Silva JH, Morio B, Góis Leandro C, Pirola L. Maternal low protein diet induces persistent expression changes in metabolic genes in male rats. World J Diabetes 2020; 11(5): 182-192
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v11/i5/182.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v11.i5.182