Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Diabetes. Apr 15, 2020; 11(4): 126-136
Published online Apr 15, 2020. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v11.i4.126
Published online Apr 15, 2020. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v11.i4.126
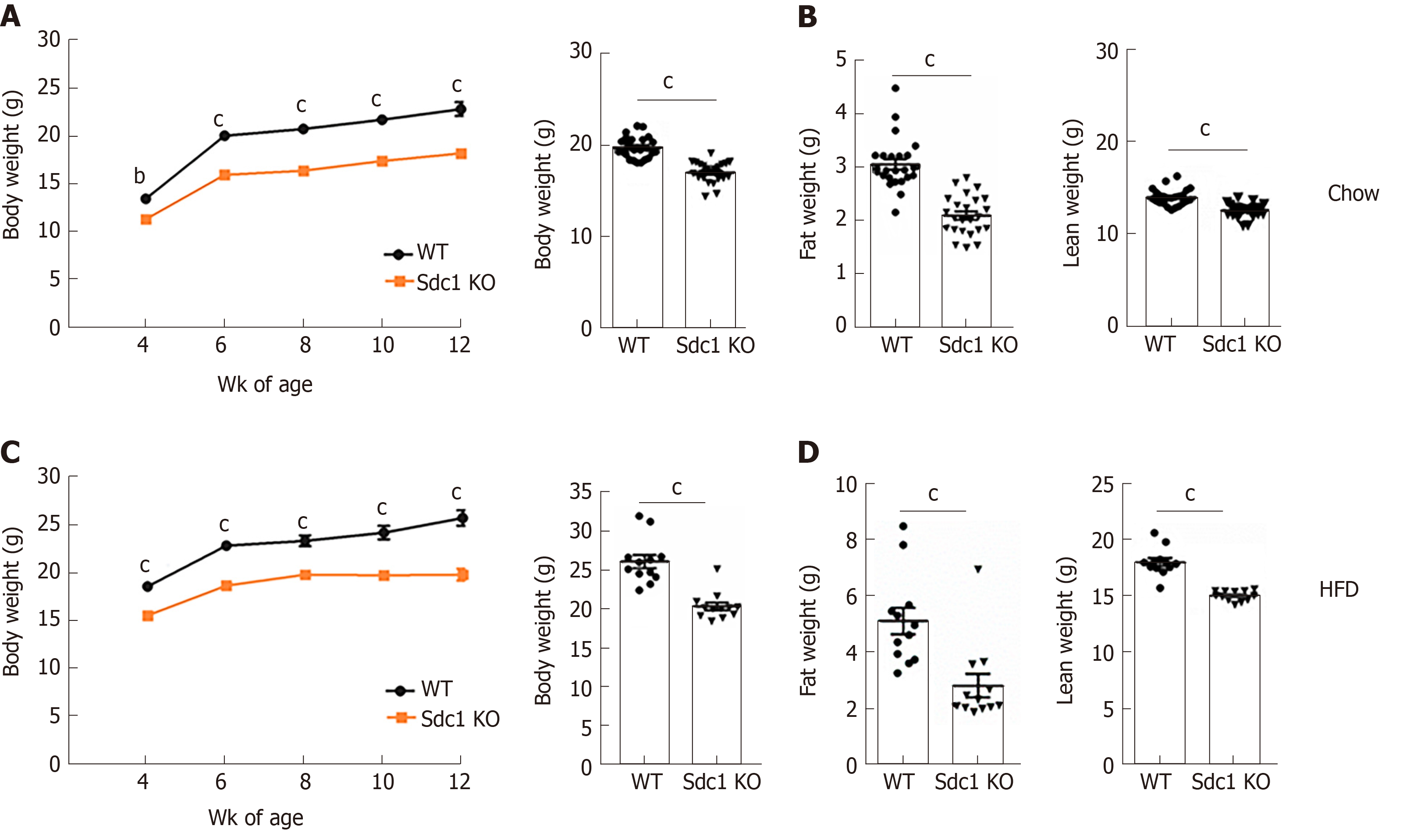
Figure 1 Effect of syndecan-1 deletion on body weight and fat content.
A, B: Age-matched Sdc1 knockout (Sdc1 KO) and wild type (WT) mice were fed either chow diet or high-fat diet for indicated periods. Sdc1 KO mice maintained their body weight overtime than WT mice. There was significant difference in total body weight, fat mass and lean mass of chow-fed Sdc1 KO mice compared with WT mice; C, D: Like, chow diet fed mice, high-fat diet fed mice also maintained the difference in body weight, fat mass and lean mass. Bar graphs show cumulative data from two independent experiment of total 24 female BALB/c mice and represents mean ± SE of 12-24 animals of each genotype. bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. Sdc1 KO: Sdc1 knockout; HFD: High-fat diet; WT: Wild type.
- Citation: Jaiswal AK, Sadasivam M, Aja S, Hamad ARA. Lack of Syndecan-1 produces significant alterations in whole-body composition, metabolism and glucose homeostasis in mice. World J Diabetes 2020; 11(4): 126-136
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v11/i4/126.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v11.i4.126