Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Diabetes. Dec 15, 2020; 11(12): 622-643
Published online Dec 15, 2020. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v11.i12.622
Published online Dec 15, 2020. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v11.i12.622
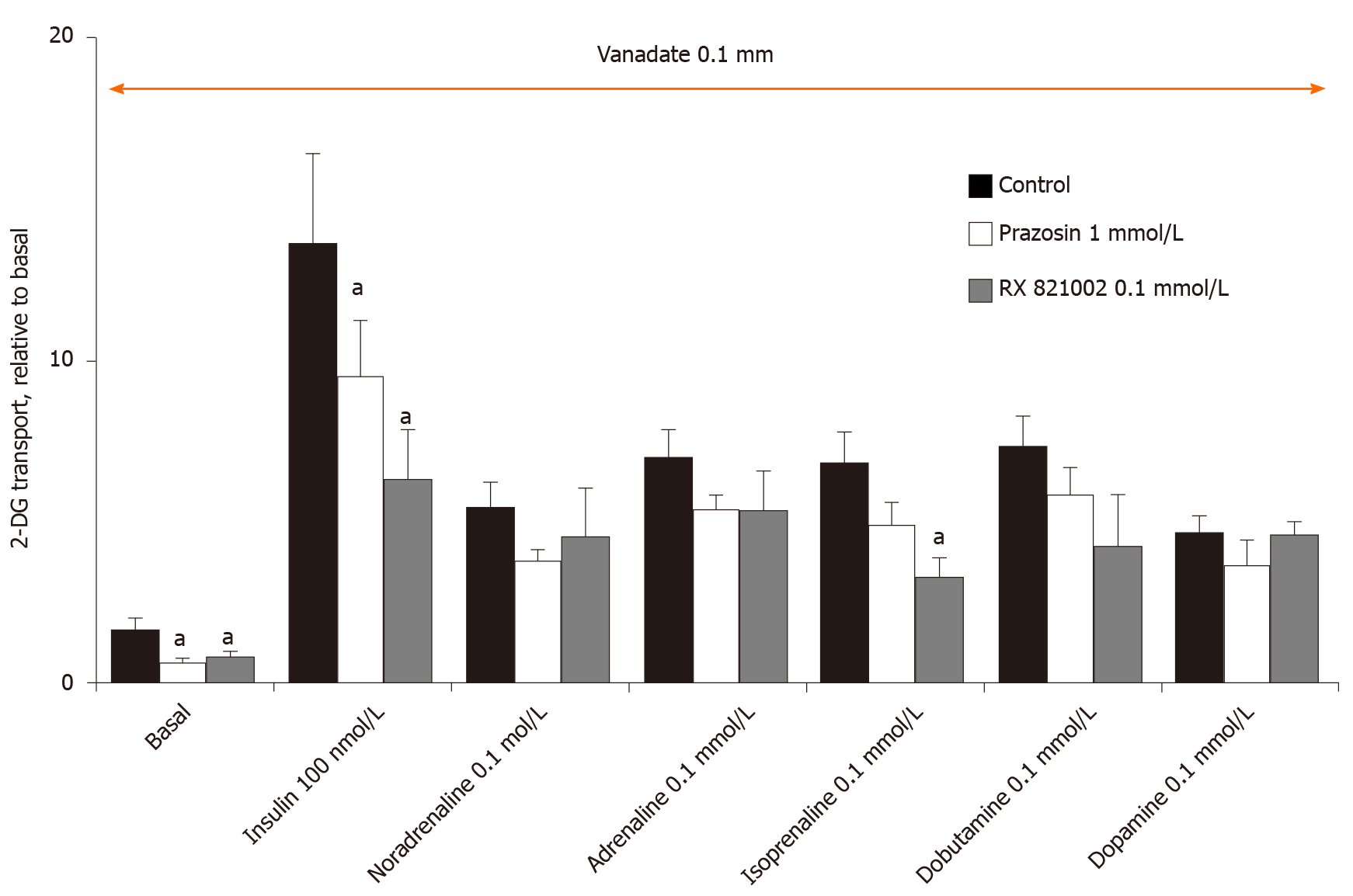
Figure 7 Inhibition of basal and insulin-stimulated hexose uptake in rat adipocytes by high doses of the α1-adrenoreceptors antagonist prazosin and the α2-adrenoreceptors antagonist methoxy-idazoxan.
Rat fat cells were incubated for 45 min with the indicated concentrations of agents without (control, closed columns), and with 1 mmol/L prazosin (open columns) or 0.1 mmol/L RX 821002 (shaded columns) prior to 2-deoxyglucose uptake, expressed as the fold increase relative to basal. The mean ± SE of 4 separate experiments performed in the presence of 100 µmol/L vanadate was determined. Significant difference between the inhibitor and the respective control was observed at: aP < 0.05. 2-DG: 2-Deoxyglucose.
- Citation: Fontaine J, Tavernier G, Morin N, Carpéné C. Vanadium-dependent activation of glucose transport in adipocytes by catecholamines is not mediated via adrenoceptor stimulation or monoamine oxidase activity. World J Diabetes 2020; 11(12): 622-643
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v11/i12/622.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v11.i12.622