Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Diabetes. Dec 15, 2020; 11(12): 622-643
Published online Dec 15, 2020. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v11.i12.622
Published online Dec 15, 2020. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v11.i12.622
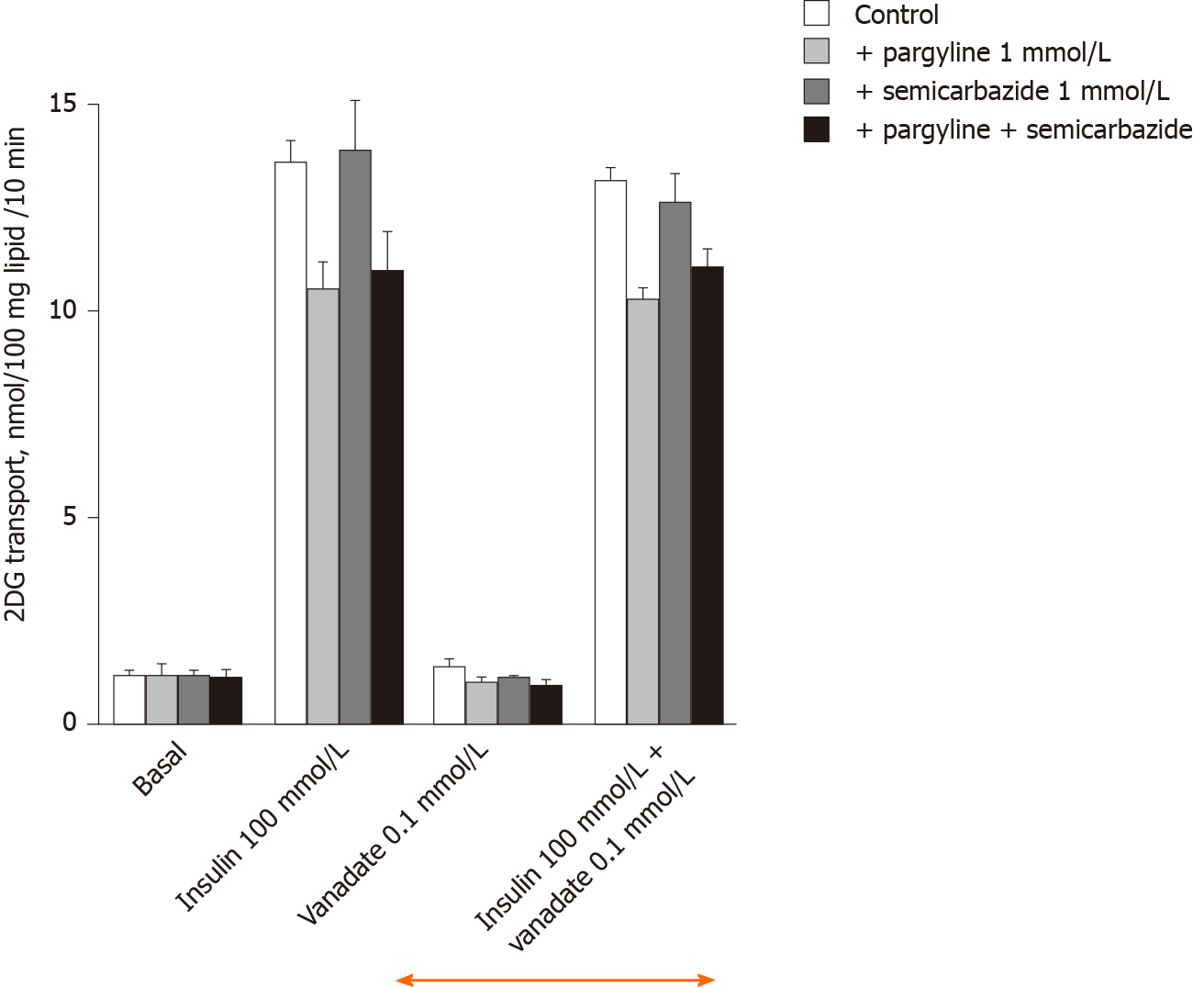
Figure 2 Lack of influence of amine oxidase inhibitors and of 100 µmol/L vanadate on basal and insulin-stimulated hexose uptake in rat adipocytes.
Rat fat cells (approximately 18 mg lipid/400 µL) were incubated for 45 min with the indicated concentrations of agents without (control, open columns), or with 1 mmol/L pargyline and 1 mmol/L semicarbazide, respectively (grey columns) or in combination (dark columns); then [3H]-2-deoxyglucose uptake (2-DG) was assayed over a 10-min period. The mean ± SE of 4 separate experiments was determined. There was no significant difference between inhibitors and each respective control. Similarly, no difference was found between corresponding conditions (basal or 100 nmol/L insulin-stimulated 2-DG transport) without (left) and with 100 µmol/L vanadate (right, above orange arrow) by the paired t test. 2-DG: 2-Deoxyglucose.
- Citation: Fontaine J, Tavernier G, Morin N, Carpéné C. Vanadium-dependent activation of glucose transport in adipocytes by catecholamines is not mediated via adrenoceptor stimulation or monoamine oxidase activity. World J Diabetes 2020; 11(12): 622-643
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v11/i12/622.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v11.i12.622