Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Diabetes. Dec 15, 2019; 10(12): 546-559
Published online Dec 15, 2019. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v10.i12.546
Published online Dec 15, 2019. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v10.i12.546
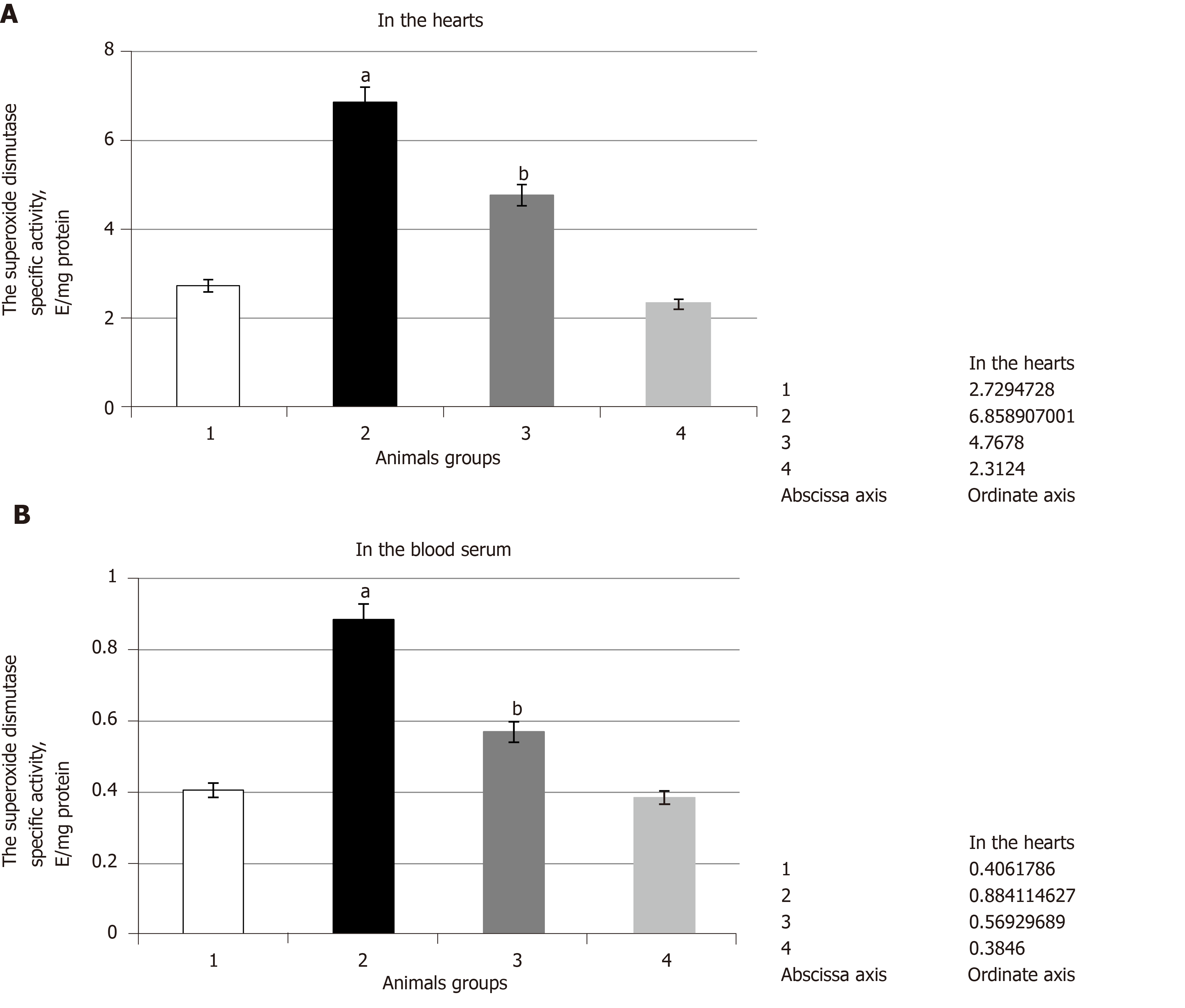
Figure 2 The superoxide dismutase specific activity, E/mg protein in the rats' hearts, and the blood serum during the development of experimental hyperglycemia.
A: The superoxide dismutase (SOD) specific activity, E/mg protein in the rats' hearts during the development of experimental hyperglycemia; B: The SOD specific activity, E/mg protein in the blood serum during the development of experimental hyperglycemia. 1: Control group; 2: Animals with experimental hyperglycemia mellitus induced by streptozotocin; 3: 10-(6-plastoquinonyl) decyltriphenylphosphonium (SkQ1) is administered to animals at pathology; 4: SkQ1 is administered to animals at control group. aP ≤ 0.0167 compared with control; bP ≤ 0.0167 compared with pathology. SkQ1: 10-(6-plastoquinonyl) decyltriphenylphosphonium.
- Citation: Agarkov AA, Popova TN, Boltysheva YG. Influence of 10-(6-plastoquinonyl) decyltriphenylphosphonium on free-radical homeostasis in the heart and blood serum of rats with streptozotocin-induced hyperglycemia. World J Diabetes 2019; 10(12): 546-559
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v10/i12/546.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v10.i12.546