Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Diabetes. Nov 15, 2019; 10(11): 517-533
Published online Nov 15, 2019. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v10.i11.517
Published online Nov 15, 2019. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v10.i11.517
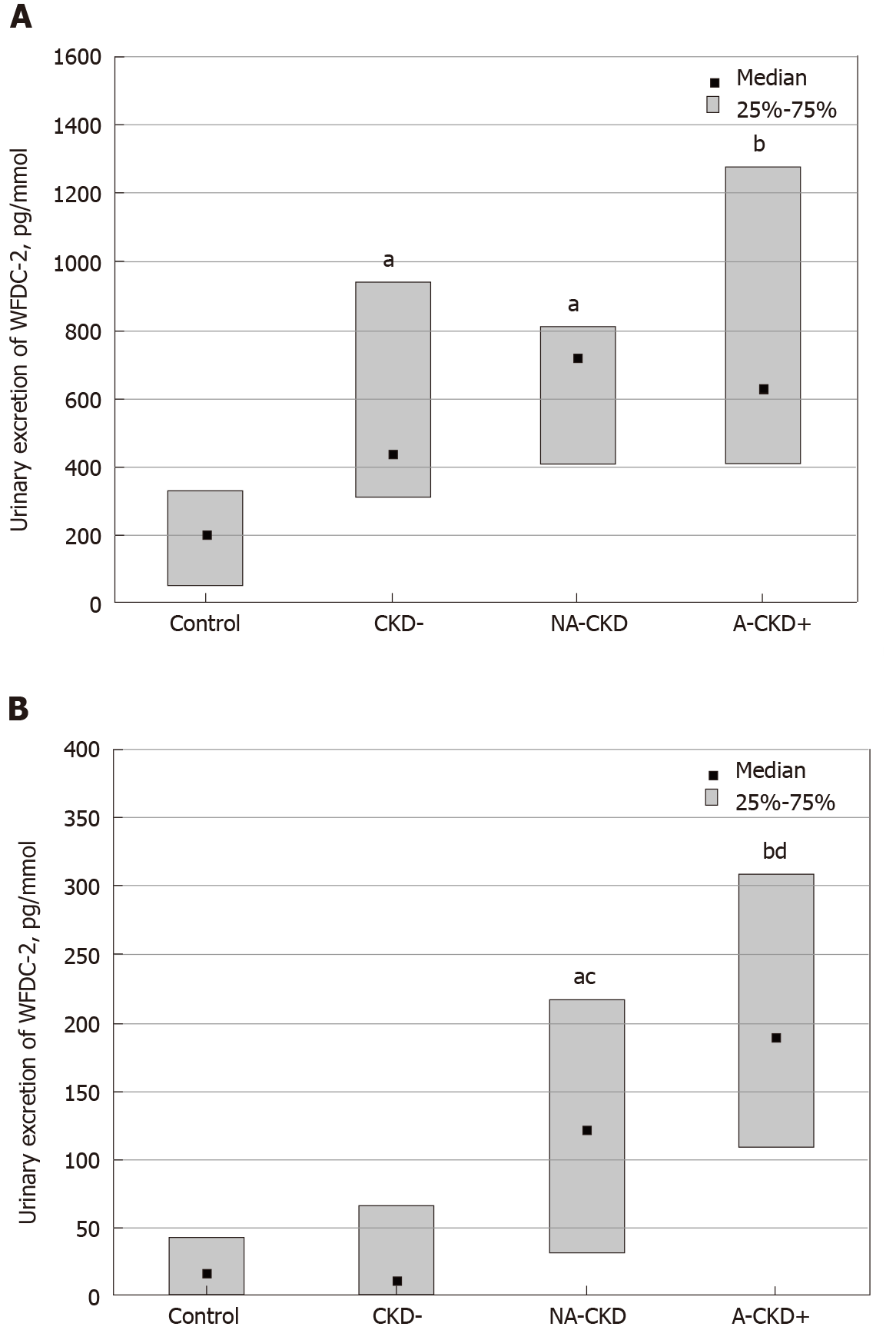
Figure 3 Urinary excretion of WAP-four-disulfide core domain protein 2 in individuals with type 2 diabetes and different patterns of chronic kidney disease.
A: Males; B: Females. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs non-diabetic control, cP < 0.05, dP < 0.01 vs СKD– group (the test of multiple comparisons of mean ranks). CKD–: The group of individuals with estimated glomerular filtration rate ≥ 60 mL/min × 1.73 m2 and urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio < 3.0 mg/mmol; NA-CKD: Non-albuminuric chronic kidney disease, the group of individuals with estimated glomerular filtration rate < 60 mL/min × 1.73 m2 and urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio < 3.0 mg/mmol; A-CKD–: Group of patients with estimated glomerular filtration rate ≥ 60 mL/min × 1.73 m2 and urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio ≥ 3.0 mg/mmol; A-CKD+: Group of individuals with estimated glomerular filtration rate < 60 mL/min × 1.73 m2 and urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio ≥ 3.0 mg/mmol.
- Citation: Korbut AI, Klimontov VV, Vinogradov IV, Romanov VV. Risk factors and urinary biomarkers of non-albuminuric and albuminuric chronic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes. World J Diabetes 2019; 10(11): 517-533
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v10/i11/517.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v10.i11.517