Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Diabetes. Nov 15, 2016; 7(19): 547-553
Published online Nov 15, 2016. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v7.i19.547
Published online Nov 15, 2016. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v7.i19.547
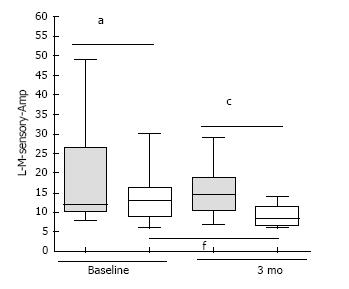
Figure 1 Amplitude in sensory component of Left Median nerve at baseline and 3 mo (Shaded bar: Pioglitazone arm; White bar: Non pioglitazone arm).
aP = 0.496, cP = 0.002 (Mann-Whitney U Test); fP = 0.01 (Wilcoxon matched pairs signed rank sum test). L-M-sensory-Amp: Amplitude in sensory component of Left Median nerve.
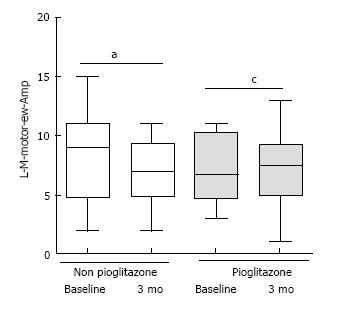
Figure 2 Amplitude in motor component of Left Median nerve in the segment between elbow and wrist at baseline and 3 mo (Shaded bar: Pioglitazone; White bar: Non pioglitazone arm).
aP = 0.049, cP = 0.964 (Wilcoxon matched pairs signed rank sum test). L-M-motor-ew-Amp: Amplitude in motor component of Left Median nerve in the segment between elbow and wrist.
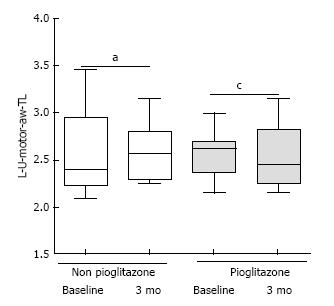
Figure 3 Terminal Latency in motor component of Left Ulnar nerve across wrist at baseline and 3 mo (Shaded bar: Pioglitazone; White bar: Non pioglitazone arm).
aP = 0.043, cP = 0.055 (Wilcoxon matched pairs signed rank sum test). L-U-motor-aw-TL: Terminal Latency in motor component of Left Ulnar nerve across wrist.
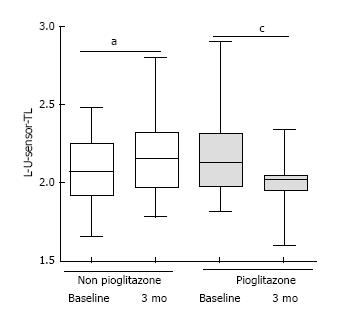
Figure 4 Terminal Latency in sensory component of Left Ulnar nerve at baseline and 3 mo (Shaded bar: Pioglitazone; White bar: Non Pioglitazone arm).
aP = 0.161, cP = 0.038 (Wilcoxon matched pairs signed rank sum test). L-U-sensory-TL: Terminal Latency in sensory component of Left Ulnar nerve.
- Citation: Chatterjee S, Sanyal D, Das Choudhury S, Bandyopadhyay M, Chakraborty S, Mukherjee A. Effect of pioglitazone on nerve conduction velocity of the median nerve in the carpal tunnel in type 2 diabetes patients. World J Diabetes 2016; 7(19): 547-553
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v7/i19/547.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v7.i19.547