Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Mar 15, 2016; 8(3): 248-257
Published online Mar 15, 2016. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v8.i3.248
Published online Mar 15, 2016. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v8.i3.248
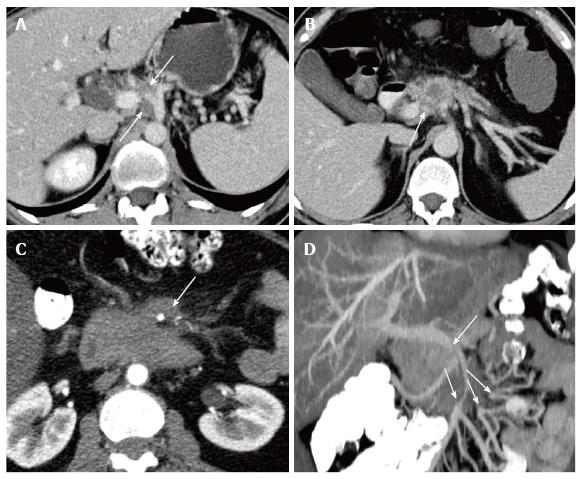
Figure 1 Examples of resecatability assessment in untreated pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma by means of computed tomography.
A: Unresectability due to encasement of the common hepatic artery reaching to the celiac trunc (arrows); B: Borderline respectability with infiltration of the portal vein and one-sided contact to the common hepatic artery without extension to the celiac trunc. Neoadjuvant treatment and/or pancreatic left resection with en-bloc resection of the celiac trunc (after embolization) can be considered; C: Unresectability due to encasement of the superior mesenteric artery by more than 180º; D: Infiltration of the superior mesenteric vein and venous confluence with stenosis and multiple separated mesenteric venous branches unsuitable for surgical reconstruction.
- Citation: Sinn M, Bahra M, Denecke T, Travis S, Pelzer U, Riess H. Perioperative treatment options in resectable pancreatic cancer - how to improve long-term survival. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2016; 8(3): 248-257
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v8/i3/248.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v8.i3.248