Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Oct 15, 2015; 7(10): 184-203
Published online Oct 15, 2015. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v7.i10.184
Published online Oct 15, 2015. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v7.i10.184
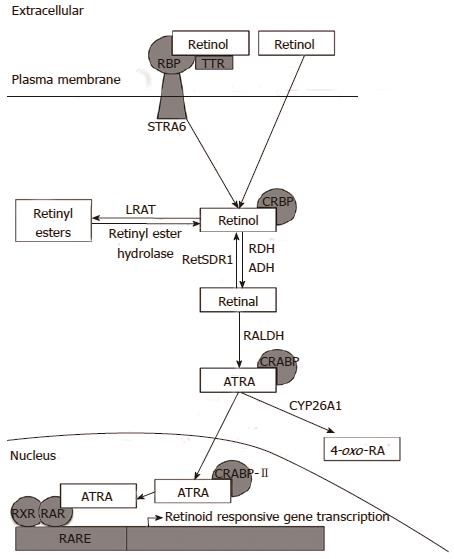
Figure 1 Retinoid metabolism.
Vitamin A circulates as retinol bound to RBP and TTR. Retinol can be absorbed into cells via STRA6 or diffusion through the cell membrane. Intracellularly, retinol can be stored as retinyl esters or converted to ATRA. ATRA travels to the nucleus where it binds RAR to induce the transcription of retinoid-responsive genes. RBP: Retinol binding protein; TTR: Transthyretin; STRA6: Stimulated by retinoic acid 6; CRBP: Cellular retinol binding protein; LRAT: Lecithin retinol acyltransferase; RALDH: Retinaldehyde dehydrogenase; CRABP: Cellular retinoic acid binding protein; CYP26A1: Cytochrome P450 26A1; 4-oxo-RA: 4-oxo-retinoic acid; ATRA: All-trans-retinoic acid; RXR: Retinoid X receptor; RAR: Retinoic acid receptor; RARE: Retinoic acid response element.
- Citation: Applegate CC, Lane MA. Role of retinoids in the prevention and treatment of colorectal cancer. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2015; 7(10): 184-203
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v7/i10/184.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v7.i10.184