Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Jul 15, 2014; 6(7): 225-243
Published online Jul 15, 2014. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v6.i7.225
Published online Jul 15, 2014. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v6.i7.225
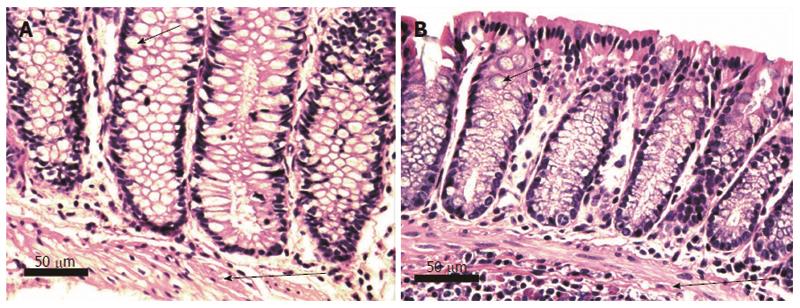
Figure 5 Histologically normal human (A) and mouse (B) colonic crypts, cut along the long axis of crypts.
The normal human and mouse glands (crypts) are composed of columnar epithelial cells and goblet cells. Short arrows indicate typical goblet cells containing mucin (not stained, white in the image). About half of the cells in the crypts are goblet cells. Nuclei are darkly stained. All crypts are normally aligned colonic mucosal glands with the bases of the crypts abutting the muscularis mucosa. Long arrows indicate the muscularis mucosa. All crypt cells are parallel to each other and the nuclei are adjacent to each other, with no overlapping. Images obtained with 40× objective lens.
- Citation: Prasad AR, Prasad S, Nguyen H, Facista A, Lewis C, Zaitlin B, Bernstein H, Bernstein C. Novel diet-related mouse model of colon cancer parallels human colon cancer. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2014; 6(7): 225-243
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v6/i7/225.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v6.i7.225