Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Jul 15, 2013; 5(7): 115-126
Published online Jul 15, 2013. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v5.i7.115
Published online Jul 15, 2013. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v5.i7.115
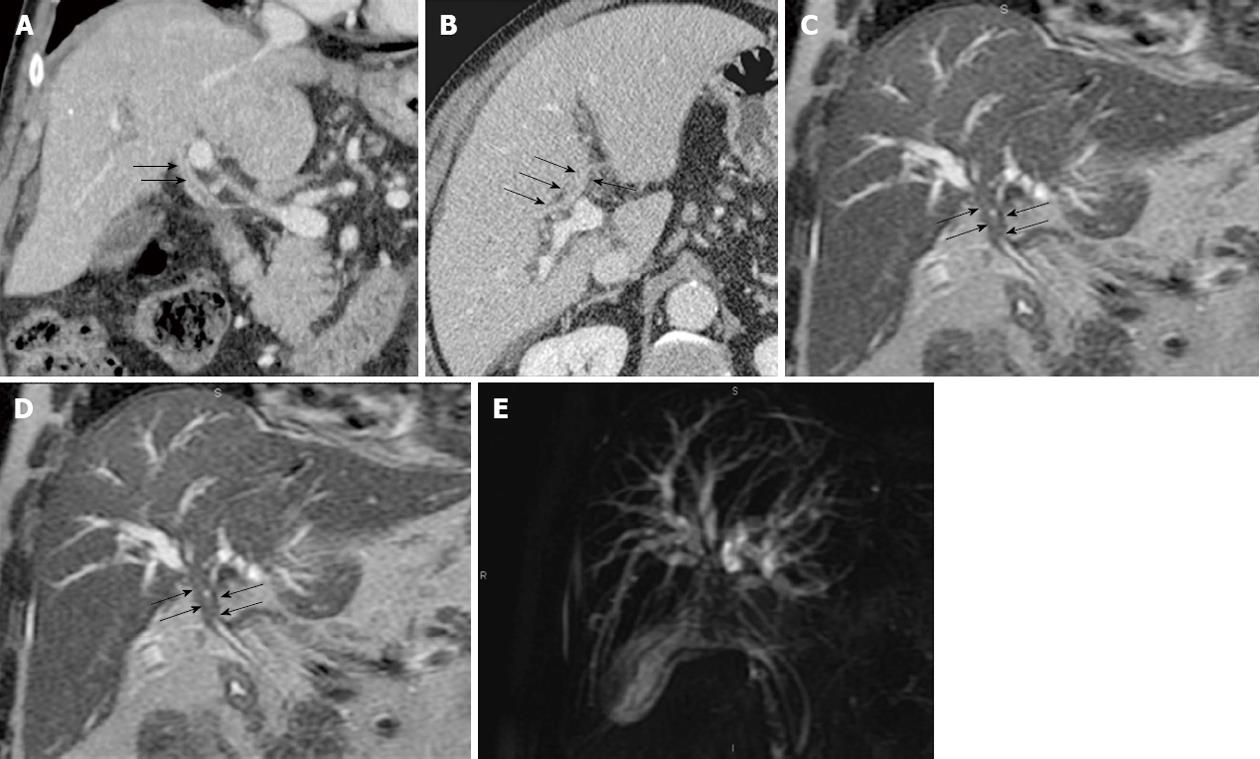
Figure 7 Lymphoplasmacytic cholangiopathy multidetector computed tomography and magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography.
A, B: Coronal reconstructed and axial multidetector computed tomography in the portal phase show periductal thickening of the common hepatic duct and hepatic bifurcation (arrows); C: Coronal thin-slab (echo spacing 4.2 ms, effective echo time 183 ms, image matrix 272 x 512, FOV 385 mm) T2-W sequence shows marked intrahepatic biliary dilatation and an abrupt stenosis of the coronary heart disease and biliary bifurcation (arrows); D: Coronal thick-slab (echo spacing 8.3 ms, effective echo time 1000 ms, image matrix 512 x 512, FOV 350 mm) magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography T2-W sequence in the same patient shows marked dilatation of intrahepatic bile ducts and a signal void in the hepatic bifurcation mimicking Klatskin tumor. Surgical exploration and histological study confirmed lymphoplasmacytic cholangiopathy.
- Citation: Valls C, Ruiz S, Martinez L, Leiva D. Radiological diagnosis and staging of hilar cholangiocarcinoma. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2013; 5(7): 115-126
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v5/i7/115.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v5.i7.115